Why can male fertility be reduced even before treatment begins?
By Ashok Agarwal, PhD; Rakesh Sharma, PhD; Edmund Sabanegh Jr., MD; and Belinda Willard, PhD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Hodgkin’s disease or Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) is a type cancer of the lymphatic system often manifested by an enlarged lymph nodes. HL may spread to adjacent lymph nodes, lungs liver or bone marrow. While the etiology of HL is still unknown, it affects a significant percentage of men of reproductive age.
Testicular cancer can be classified into germ cell, non-germ cell and extragonadal tumors. The highly prevalent germ cell tumors are further classified as either seminoma or nonseminoma, based on histological and clinical manifestations. Seminomatous germ cell tumor (SGCT) is the most common type of testicular cancer and nonseminomatous germ cell tumors (NSGCT) is an aggressive testicular germ cell tumor affecting young adults and on the increase worldwide.
While sperm banking is offered for preserving fertility potential prior to treatment of both of these diseases, we found that reduced male fertility often appears even before the start of treatment.
Until now, there have been no proteomic studies identifying changes occurring at the spermatogenic or proteomic levels that elucidate the pathophysiology of these diseases. We therefore undertook several studies to identify disease-related functions of spermatozoa proteins in men affected with HL and testicular cancer before cancer treatment.
Our goal was to identify disease-related functions of spermatozoa proteins in affected men before cancer treatment, utilizing global proteomic analysis.
Using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, we identified proteins associated with poor sperm quality in patients with HL and testicular cancer.
Advertisement
We compared samples from normal, healthy donors with cryopreserved semen samples taken before cancer treatment from men with HL, SGCT and NSGCT. With mass spectrometry analysis, we identified a number of interesting proteomic differences, including key proteins that are downregulated in men with these diseases. These key proteins are involved in spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis, acrosome reaction, oocyte binding and sperm motility function. The downregulation of these proteins may explain the impaired semen quality and fertility observed in many patients with HL, SGCT and NSGCT even before initiating cancer treatment.
Our analysis also showed that oxidative stress plays a key role in production of poor spermatozoa in these men. For instance, proteins involved in the production of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species are upregulated in the spermatozoa of men with SGCT.
Our goal now is to narrow down these key proteins and validate those that are uniquely present in lower amounts in these patients. We believe eventually these proteins may serve as biomarkers for identifying patients susceptible to these cancers.
We presented four posters from this research at the American Society for Reproductive Medicine meeting in San Antonio in October 2017.
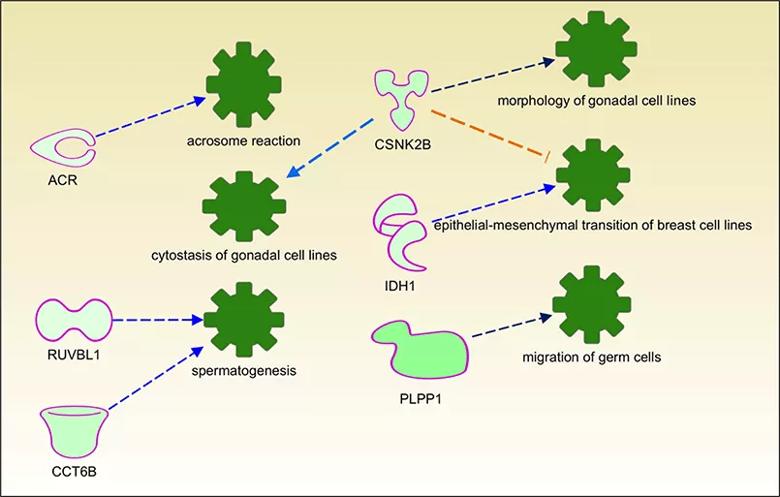
In the spermatozoa of HL patients, proteins required for acrosome reaction (ACR), spermatogenesis (RUBL1 and CCT6B), migration of germ cells (PLPP1), morphology and cytostasis of gonadal cells (CSNK2B) were downregulated compared to normal controls.
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
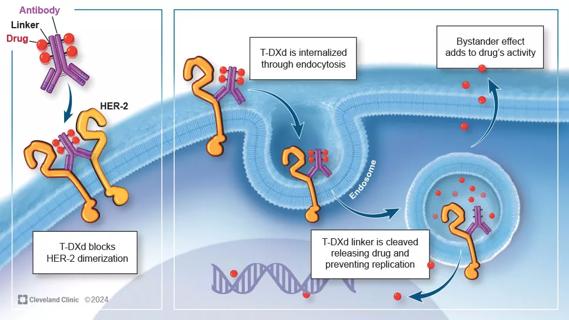
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients