What sets this new imaging method apart, and how it's changing practice
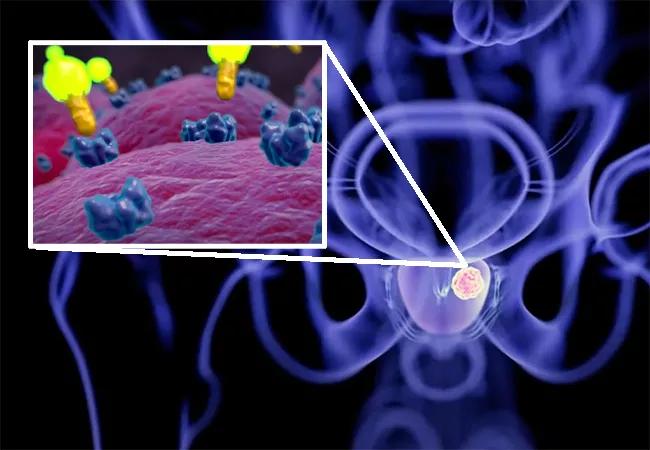
Accurate imaging is a critical component of prostate cancer management for a number of reasons, including tumor localization, disease staging, and detecting recurrence. PSMA PET scan — named a top medical innovation by Cleveland Clinic in 2022 — offers a new imaging approach for this patient population that has the ability to detect recurrence earlier and, in turn, enable clinicians to implement treatment sooner.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“PSMA imaging is an exciting innovation that holds significant promise for the treatment of prostate cancer,” notes Rahul Tendulkar, MD, a radiation oncologist at Cleveland Clinic. “To better tailor treatments for our patients, we must be able to stratify risk and accurately determine disease stage. Therefore, imaging capabilities are a key component of managing these patients successfully.”
The conventional imaging methods typically used for prostate cancer patents, including CT, MRI, and bone scan, have limitations when it comes to disease detection, according to Steve Huang, MD, Nuclear Medicine Department, Cleveland Clinic.
Compared with other imaging options, PSMA PET scan has greater sensitivity and can detect metastases sooner, allowing clinicians to better serve patients and make treatment decisions earlier, he says. “PSMA PET scan makes it possible to see a smaller volume of prostate cancer cells, which allows oncologists to localize the disease and determine the best approach to treatment.”
“PSMA, or prostate-specific membrane antigen, is a protein on the surface of many prostate cancer cells, and it has been shown that radiotracers targeting PSMA can identify early, low-volume sites of lymph node or distant metastases of prostate cancer,” says Dr. Tendulkar.
The first PSMA-targeted PET imaging drug for prostate cancer—gallium 68 PSMA-11 (Ga 68 PSMA-11) — was approved by the FDA in 2020 for patients with suspected prostate cancer recurrence and metastasis. This approval was based on phase 3 clinical trials that demonstrated a significant increase in accuracy for the detection of prostate cancer compared with standard imaging modalities. In 2021, a second FDA approval followed for Pylarify® (piflufolastat F-18) for the same indication.
Advertisement
Several institutions have adopted this technology since, including Cleveland Clinic, which integrated PSMA PET scans into practice in September 2021. However, this is not a new area of interest for experts at the facility. Warren Heston, PhD, a basic scientist at Cleveland Clinic Lerner Research Institute, first discovered and cloned the PSMA protein in the early 1990s. Researchers have also participated in clinical trials evaluating the PSMA imaging agent rhPSMA-7.3 (18F).
While use of this approach has only recently started in clinical practice, Dr. Tendulkar has already observed a shift in the management of prostate cancer patients at Cleveland Clinic.
“Our ability to obtain PSMA PET scans has really been a game changer, and I don’t use that term loosely,” he says. “Historically, if a patient had a rising PSA, we would get a CT scan and a bone scan. And, oftentimes, either we wouldn’t see anything obvious or, if we did, it was widespread throughout the body, at which point there’s really no curative option.
“Since integrating this new approach, we have found that PSMA PET scan can find a few sites of recurrent prostate cancer,” he continues. “And so, if we can identify recurrence before it’s widespread, we may be able to intervene earlier and perhaps alter the natural history of a patient’s disease in a way that is associated with a low risk of toxicity.”
For example, a patient who has undergone prior radiation therapy to the prostate develops a rising PSA and a local recurrence is discovered. “A PSMA PET scan that demonstrates no evidence of spread into the lymph nodes or distant metastatic sites gives us more reassurance to treat the recurrent area within the prostate in a potentially curative fashion for a second chance of success,” says Dr. Tendulkar. “If we can be more selective in who may be treated with a salvage retreatment, we may improve our selection criteria to choose patients more likely to benefit.”
Advertisement
To date, PSMA PET scan has been used in a few hundred patients at Cleveland Clinic and there are ongoing efforts for continued growth and expansion. “There is significant demand for this technology among our patients,” says Dr. Huang, who notes that they are currently scheduling about one month out. “Given the potential impact of this approach, increasing access to PSMA PET scans is a top priority. We are working hard to open more scanning sites and expand the availability throughout our system.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
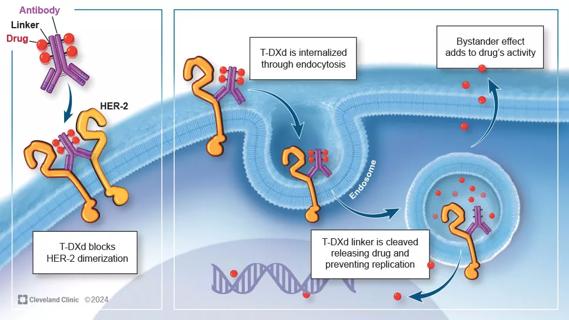
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients