Cell study upends thinking about VEGF-A

A protein has been identified that inhibits the growth of cancerous tumors and slows development of new blood vessels that allow cancers to spread. The protein is a variant of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), a substance known to promote cancer growth. The researchers named the variant VEGF-Ax. The protein cuts off the blood supply to tumors and inhibits tumor development in animal models. It could have major implications for the use of existing anti-VEGF therapies and the development of new drugs.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The findings were made by a team led by Paul Fox, PhD, of Cleveland Clinic’s Lerner Research Institute, and were published in Cell. “It is truly remarkable that a small change in a protein sequence leads not just to a protein with a different function, but one with a function completely opposite to the original,” says Dr. Fox. “In the context of cancer, the small extension changes a very ‘bad’ protein into a very ‘good’ one.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
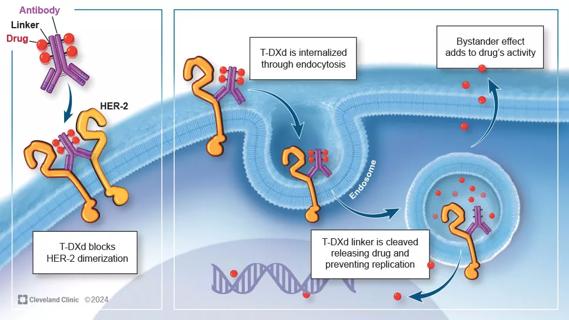
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients