Study highlights value of preoperative imaging to guide surgical decision-making
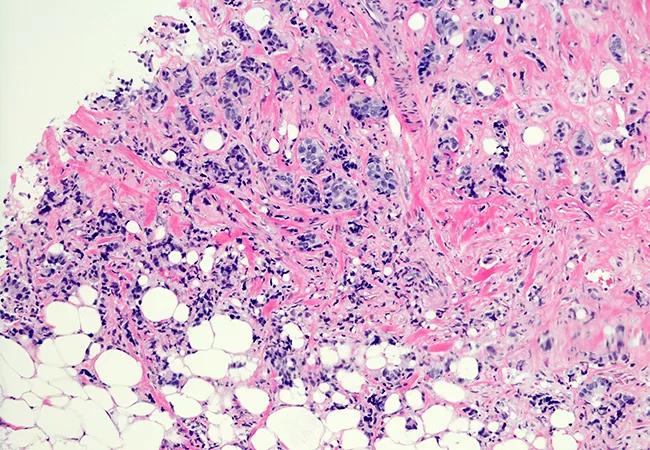
A new Cleveland Clinic study explores the role of MRI for assessing the extent of disease in patients with invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC), a distinct subset of cancer that is notoriously difficult to stage. Accounting for 15% of breast cancers, ILC is associated with a uniquely high rate of multifocal/multicentric and bilateral disease – a risk that highlights the importance of diagnostic precision.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“The ability to accurately assess for disease extent and lymph node involvement is paramount for counseling patients on appropriate treatment and predicting outcomes in patients with ILC,” explains Megan L. Kruse, MD, study co-author and a breast medical oncologist at Taussig Cancer Institute.
The study, published in the Annals of Surgical Oncology, analyzed the imaging modalities used to clinically stage patients and then compared clinical and pathologic tumor and nodal staging based on the imaging used.
“The data further reinforce the significant role that MRI can play in preoperative planning,” says Dr. Kruse. “Importantly, while tumor size was better defined on MRI in most cases, 30% of patients with ILC were found to have imaging occult-positive lymph nodes. This suggests that, while MRI is likely helpful for many patients with ILC, challenges remain. It is important to discuss the limitations of imaging with patients so that they are prepared for the potential of tumor upstaging based on surgical pathology results.”
This study is a retrospective analysis comparing the clinical and pathologic staging results for 692 patients who received a diagnosis of ILC between 2004 and 2017. The study cohort included 43 patients (6%) with a diagnosis of contralateral breast cancer (CBC) and 232 patients (33%) with a diagnosis of multifocal/multicentric disease at presentation. Follow-up details, including local recurrence, metastatic recurrence and survival, were evaluated.
Preoperative MRI was obtained in 66% of patients; younger patients underwent MRI with greater frequency (P < 0.001). MRI identified additional disease in 20% of patients. Specifically, 56% of CBC and 29% of multicentric/multifocal disease was detected only on MRI. Surgical treatment included lumpectomy (45.4%), unilateral mastectomy (40.2%) and bilateral mastectomy (14.4%).
Advertisement
Patients who had a preoperative MRI had a similar clinical and pathologic T stage (size) estimate, whereas those without MRI had a T stage that was underestimated clinically (upstage rate, 16% MRI vs. 30% no MRI). Researchers noted a significant discordance in clinical and pathologic nodal staging.
Clinical staging identified 14% of patients with a positive lymph node; however, pathologic positive lymph nodes were identified in 35% of patients. Moreover, 30% of patients with clinically negative lymph nodes (cN0) on initial workup were found to have at least one positive lymph node during surgery, with 6.7% of cN0 and 60% of cN1 upstaged to N2/N3 disease on final pathology.
Although preoperative MRI helped clinicians identify additional disease in 20% of cases and more accurately predicted tumor size staging, it did not improve the prediction of pathologic nodal staging. At the six-year follow-up evaluation, a local recurrence had developed in 2.3% of patients, and distant metastases were detected in 9.4%. The overall survival rate was 96% at three years and 91% at five years.
“Another important aspect of the study is that patients with invasive lobular cancer did not have a higher rate of contralateral breast cancer. Contralateral breast cancer is something historically thought to be more common in patients with ILC, and this study showed this to be false,” explains Stephanie Valente, DO, study co-author and Director of the Cleveland Clinic West Region Breast Program. “This should be taken into consideration when discussing contralateral prophylactic mastectomy for unilateral disease.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
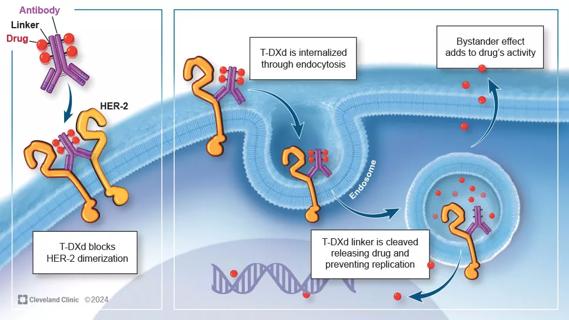
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients