Study reports on 11-year experience in AML
A multicenter study involving two cohorts of patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) found that less-intensive therapies for AML are associated with increased mortality in risk groups defined by age, comorbidities and cytogenetics. The study was published in the August 2021 issue of the journal Blood.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Aaron T. Gerds, MD, MS, hematologist in Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center’s Leukemia & Myeloid Disorders Program and a study co-author, says that these findings add to the ongoing conversation about the care of patients with AML, which is focused on moving away from intensive induction chemotherapy and towards a less-intensive treatment combination.
“For a long time, we’ve had a dichotomous choice in AML treatments: either super heavy-duty induction chemotherapy, also known as 7+3, or less-intensive therapies like azacitidine,” he says. “So, it really was one or the other.” However, with the more recent drug approvals in AML, he adds, prescribing has shifted toward less-intensive therapies and avoiding the toxicities associated with induction chemotherapy such as strong myelosuppression, and the need for transfusions and hospitalization.
The purpose of the study was to gain a better understanding of the impact of treatment intensity on survival and quality of life (QOL) in AML by comparing the outcomes after less-intensive versus intensive induction therapies in two different patient cohorts. It included 1292 patients from a multicenter retrospective cohort treated at six institutions between 2008 and 2012 and 695 patients from a prospective cohort treated at 13 institutions between 2013 and 2017. Patients from the retrospective cohort who received less-intensive therapies were older and had more comorbidities, as well as worse Karnofsky performance status and more adverse cytogenetics. Investigators used the AML composite model to define three distinct prognostic groups by assigning higher scores to older age, comorbidity burden and adverse cytogenetic risks.
Advertisement
“In the retrospective portion of this multi-site, 11-year experience we actually saw better overall survival (OS) for intensive chemotherapy — the 7 + 3 regimen — as compared with less-intensive therapies in all patients,” says Dr. Gerds. “This was the main focus — patients over the age of 65 that could potentially have comorbidities are often given less-intensive therapies in everyday practice. Here, they actually didn’t do as well with this approach [with respect to OS] as if they were given intensive chemotherapy.”
In the prospective cohort analysis, which included patients from the same institution, OS was also better for patients who received intensive therapy. However, when the models were adjusted for age, chance of cure and physician-assigned Karnofsky performance score, the risk of mortality and QOL were similar between the two treatment groups.
Although these latest findings are a valuable addition to the existing knowledge about induction therapies for AML, the lack of definitive answers means the debate on optimal AML induction therapy will continue. Dr. Gerds believes that randomized trials would be needed to further decipher the risks and benefits of specific therapies.
“Although the field is moving in the direction of not as readily offering intensive therapies to older patients, there’s still value in it,” he says. “In the absence of a large randomized controlled trial, I think that there will be this tension [among experts in the field]. In our retrospective portion we’ve shown a clear advantage for intensive therapies, even in older-age patients. And in the prospective study there was clearly no survival or QOL advantage, other than the length of hospitalization, for less-intensive therapies.”
Advertisement
Another ongoing challenge in AML care is the absence of a specific tool to help the treating clinician choose the best treatment option with a strong degree of certainty. The optimal course of treatment is often a joint decision between the patient and their provider, and is based on the discussion of risks, benefits and personal preferences.
“There’s no widely-accepted model, or predictor, that they can plug in, and say you should get this treatment, or you should get that treatment,” he says. “That’s why there is all this debate, and why this paper is really important, because it suggested that even older and frailer patients can benefit from intensive chemotherapy.”
The study also raised a discrepancy in the patient and clinician perceptions of the “chance of cure,” an important aspect of AML care that clinicians should recognize, Dr. Gerds says. “Part of the treatment decision is the chance of cure. And if there is a discrepancy in the perception of what the treating doctor and the patient are thinking, I think that’s really important and needs to be unpacked further.”
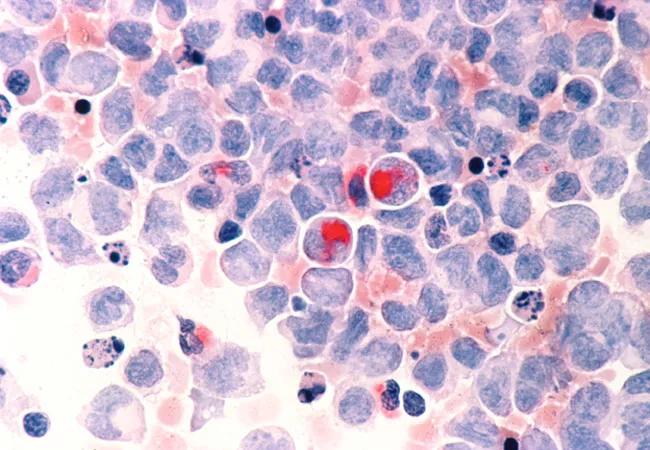
Image: Human cells with acute myelocytic leukemia (AML) in the pericardial fluid, shown with an esterase stain at 400x. Source: NCI Visuals Online.
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
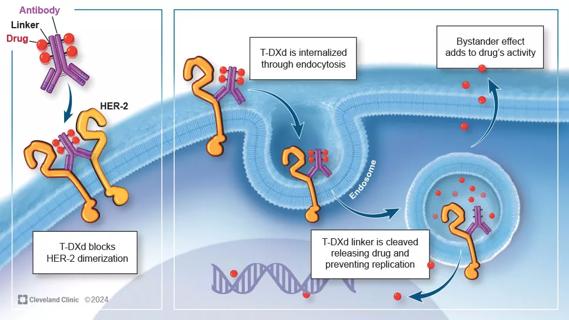
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients