May reduce tumor size, reopen the possibility of surgery
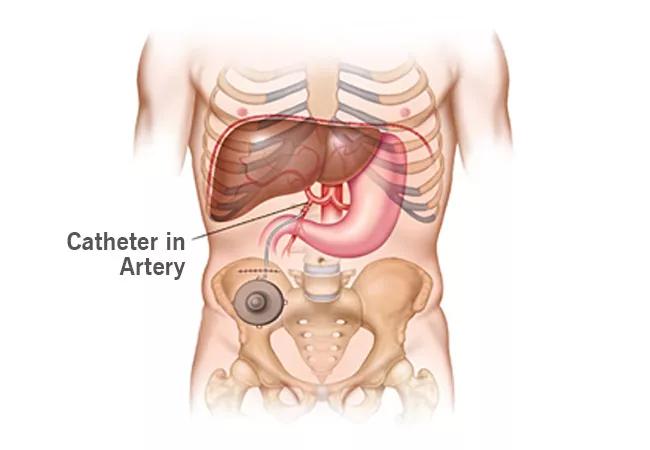
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/4faf10fe-973d-4d2d-b417-155d05af9659/17-DDI-152-Hepatic-Artery-Chemo-CQD-4_jpg)
17-DDI-152-Hepatic-Artery-Chemo-CQD-4
Colorectal cancer is a worldwide healthcare problem, representing the third leading cause of cancer related death in the United States. About 50 percent of patients will develop metastasis, and liver resection stands as the mainstay therapy associated with 25 to 60 percent five-year survival. On the other hand, for patients who have colorectal cancer with liver metastases (CRLM) that cannot be surgically removed, long-term survival rates are abysmal — just 10 percent of patients live five years beyond diagnosis of non-resectable CRLM.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In response to this, Cleveland Clinic has started offering a new regional-directed chemotherapy option, which can offer the possibility of reducing tumor size and reopening the possibility of surgery. Directed chemo-infusion to the liver through a surgically implantable pump is a complementary therapy option that can convert non-resectable CRLM to resectable disease, delivers superior local tumor control, can prevent recurrence of metastases after being removed, and can improve patient survival.
“There is definitely benefit to this, and it is one more option we offer because we see the value for patients who fit the appropriate qualifications,” says Federico Aucejo, MD, Surgical Director of Cleveland Clinic’s Liver Tumor Clinic, who has implanted several devices. “It can improve survival by converting patients into surgical candidates and by preventing recurrence of disease.”
The implanted pump supplies high-dose chemotherapy directly to the disease site via catheterization of the gastroduodenal artery, and can reduce tumors to operable size with more favorable results and fewer side effects than systemic treatment.
The primary benefit of this approach is that we can administer higher doses of chemotherapy directly to the cancer site than would be possible using traditional systemic treatment. As an added benefit and because chemotherapy is delivered directly into the liver, drugs are metabolized quickly and eliminated from the system with fewer side effects.
Studies have shown that as many as 74 percent of patients with non-resectable CRLM respond in some measurably favorable way to hepatic artery chemo-infusion.
Advertisement
Hepatic artery chemotherapy through implantable pump is now part of the large armamentarium of therapies offered to patients with liver cancer through Cleveland Clinic’s Liver Cancer Program. Therapy options for patients with different types of liver cancer include complex liver surgery, liver transplantation, laparoscopic minimally invasive liver surgery, chemo-embolization, radio-embolization and other forms of radiotherapy, and microwave ablation.
Additionally, Cleveland Clinic’s Liver Cancer Program, under the Department of General Surgery at the Digestive Disease and Surgery Institute (DDSI), has developed a leading-edge liver cancer basic research program dedicated to discovery of new and potentially curative treatments for liver cancer.
Advertisement
Advertisement
First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses
Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels
A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials
Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
Key learnings from DESTINY trials
Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients