Bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) as a BCRL detection tool
Lymphedema is a common comorbidity of breast cancer treatment, affecting from three to five million people in the United States. Among women with advanced breast cancer, the rate of lymphedema ranges from 20 to 40 percent. Risk factors for the development of breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) include axillary lymph node dissection, radiation to the regional lymph nodes and chemotherapy.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Despite its prevalence, there is currently no standard diagnostic test for BCRL. Often, patients receive care only after visible swelling occurs in a limb or they develop symptoms. Unfortunately, when patients present with this stage of clinical BCRL, they may have higher rates of chronic BCRL and the associated quality of life detriment. “We sometimes see patients with advanced BCRL because they weren’t being followed, and, therefore, instead of presenting early in the disease process, they present with chronic advanced BCRL,” says Chirag Shah, MD, Director of Clinical Research and Breast Radiation Oncology in Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Radiation Oncology.
A growing body of evidence has shown that early detection of subclinical BCRL and subsequent early intervention improve outcomes and may reduce the need for costly, aggressive therapy such as complex decongestive physiotherapy (CDP). Additionally, recent prospective data has shown that early intervention with a short course of compression therapy reduces BCRL volume and may reduce the rates of chronic BCRL.
The multisite, international, randomized controlled PREVENT trial is investigating whether early detection of BCRL with bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) as compared with tape measurement (TM) reduces lymphedema progression.
Patients were enrolled presurgery and randomized into two surveillance groups: one using TM and the other BIS, which uses low-level electrical currents to detect the extracellular fluid in a limb, a precursor to apparent BCRL. “We surveyed the literature and found evidence for BIS as one of the best ways to detect early signs of BCRL,” says Dr. Shah, senior author of interim analysis presented at the American Society of Breast Surgeons and published in the Annals of Surgical Oncology. The study’s primary investigator is Sheila Ridner, PhD, Vanderbilt University School of Nursing.
Advertisement
The majority of the 508 patients (56.7% or 288) were diagnosed with Stage I breast cancer and 39% (198) with Stage II/III disease. They were treated with at least one of the following: mastectomy, axillary treatment (axillary lymph node dissection [ALND], sentinel lymph node biopsy [SLNB] with greater than six nodes, and axillary radiation) or taxane-based chemotherapy.
Of the 508 patients in the interim analysis, 109 participants (21.9%; 68 in the TM group, 41 in the BIS group) triggered intervention with a compression sleeve and gauntlet (glove) for four weeks. The criteria for intervention were changes from presurgical baseline of 5 to 10% by TM and 6.5 or higher L-Dex by BIS (changed from ten originally). The BIS group had a lower rate of triggers than the TM group (15.8 vs. 28.5%) and a longer time to triggering (9.5 vs. 2.8 months).
Twelve of the triggered patients progressed to CDP: 10 in the TM group (14.7%) and two (4.9%) in the BIS group. “The 10% difference between the TM and BIS groups is significant: roughly one in ten women followed with BIS didn’t need CDP who would have otherwise with tape measurement. Catching lymphedema symptoms early and intervening with a noninvasive treatment mitigated the need for a more costly, time-consuming therapy. BIS represents a validated, cost-effective, noninvasive assessment technique that can enhance patient care,” says Dr. Shah.
Cleveland Clinic is using these findings to guide its approach to lymphedema, including referring patients for prospective assessment and early intervention.
Advertisement
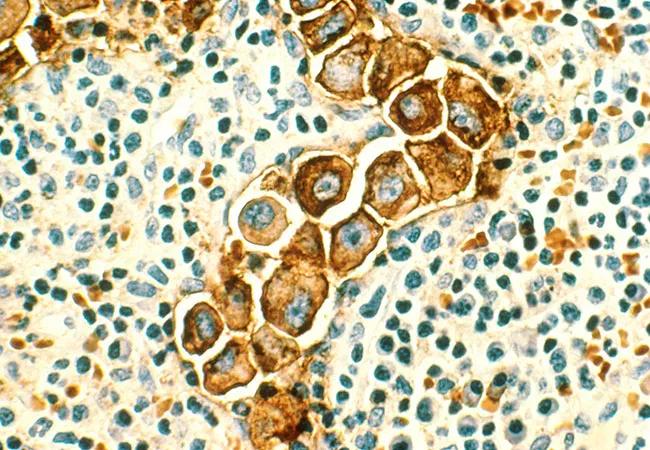
Image: Human metastatic breast cancer in the lymph nodes. Stained by immunocytochemical for epithelial membrane antigen. Magnified to 400x. Source: NCI Visuals Online.
Disclosure: Dr. Shah is a scientific consultant for ImpediMed.
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
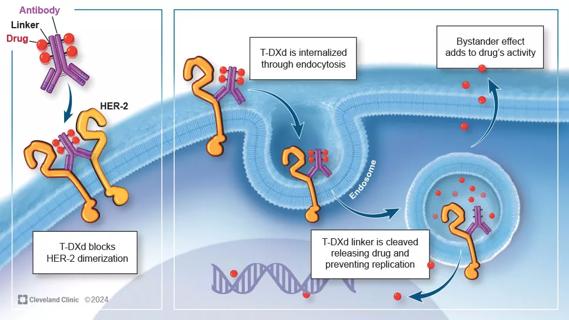
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients