Study suggests re-examining eligibility criteria for randomized controlled trials of hematologic malignancies.
As a result of overly stringent exclusion criteria, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of hematologic malignancies may be excluding specific patient population, therefore limiting trial result generalizability.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy

Considered the gold standard in medical research, RCTs play a key role in advancement of cancer treatment and are often required for regulatory approval of new drugs by the FDA.
In a recent investigation of RCTs involving hematologic malignancies, Cleveland Clinic researchers concluded that commonly accepted eligibility criteria may be inappropriately stringent, and as a result, the patient populations may not accurately reflect the typical cancer population ultimately treated with the drug.
“Landmark RCTs, with an eye to registration, may be overly conservative in using restrictive exclusion criteria,” the study concludes. “The widespread use of these criteria, many of which may not be appropriate given the toxicity profile of the investigational product, may lead to the systematic exclusion of specific patient populations, limiting the generalizability of trial results.” The study’s lead author, Abby Statler, MPH, MA, of Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center’s Research Quality Assurance Program, presented the study’s results at the 57th Annual Meeting & Exposition of the American Society of Hematology in Orlando, Fla.
Ms. Statler and her colleagues examined 98 phase II or III randomized controlled trials in hematologic malignancies that had been published in high-impact (impact factor five or greater) medical journals from January 2010 to January 2015. Of these, 32 (33 percent) were leukemia trials, 27 (28 percent) were lymphoma, 34 (35 percent) were multiple myeloma and five (5 percent) were myelodysplastic syndromes or myelofibrosis. Major drug classes studied in the trials were alkylators, antimetabolites, anthracyclines, topoisomerase inhibitors, microtubule inhibitors, proteasome inhibitors, tyrosine kinase inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies.
Advertisement
This is the first study known to actually examine eligibility criteria used in major RCTs of hematologic malignancies relevant to toxicity data of the investigational drugs.
The researchers found significant differences:
The researchers then examined whether the toxicities that were ultimately reported in the studies are appropriate given the exclusion criteria. They found significantly fewer adverse events (AE) than expected.
Assuming that study treatment leads to an AE in 10 percent of patients:
Advertisement
“The challenge is that people who have cancer also have other comorbidities and different levels of those comorbidities,” Ms. Statler says. “If the patient has a creatinine level that’s somewhat elevated, but not indicative of dramatic organ failure, then it may be appropriate to enroll that patient. Instead, eligibility criteria are often focused on ensuring that all labs are normal. That sometimes doesn’t reflect reality.
“There’s also a disconnect between the number of studies we anticipated to report toxicities given their exclusion criteria and those that actually reported them,” says Ms. Statler. Perhaps, because the patient populations included in these clinical trials are clinically fit, the likelihood these patients experience toxicities is reduced.
The reason behind having very restrictive eligibility criteria is that ultimately large phase III randomized trials are intended to demonstrate the new product’s efficacy and safety, which is a primary focus of the FDA. As a result, trials are designed to make sure that the enrolled patient population is very clinically fit.
“That does not necessarily mirror the patients who walk through our door every day,” Ms. Statler comments. “We end up excluding eligible patients because they don’t meet every single exclusion and inclusion criteria.”
In addition, once a drug is on the market, physicians may treat such patients with the drug. We need to make sure that these new drugs are in fact safe and effective in a broader group of patients,” says Ms. Statler.
Advertisement
“When designing trials, we need to be more purposeful about the eligibility criteria. We must ask whether we are using certain exclusion criteria because it is commonly accepted practice or whether it is informed by the knowledge of the toxicity profiles of the agents being investigated,” Ms. Statler concludes.
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
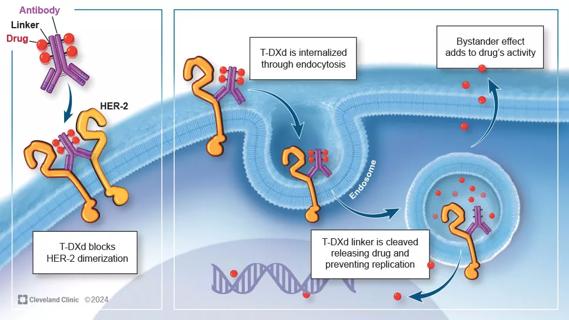
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients