Insight into the biology and future behavior of prostate tumors
Active surveillance is a reasonable option that allows physicians to monitor men with localized prostate cancer over time. How do urologists identify good candidates for active surveillance? In the past, they relied on biopsies to identify higher grade cancers. But some higher grade cancers don’t behave in an aggressive way.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
According to a recent study from the Cleveland Clinic Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, certain genomic biomarkers appear to be as important as standard clinical factors in identifying patients who are ideal candidates for surveillance or treatment at the time of diagnosis.
Researchers here have been studying genomic biomarkers and how they provide insight into the biology of cancer and its future behavior for five years. Andrew Stephenson, MD, Director, Center of Urologic Oncology, Institute Chairman Eric Klein, MD, and Chief Resident Yaw Nyame, MD, presented results of a new study at the American Urological Association’s 2018 Annual Meeting.
The researchers analyzed a prospective database of all men undergoing active surveillance at Cleveland Clinic from 2013 to 2016. To determine each tumor’s genomic score (genetic expression signature used to evaluate the clinical behavior of tumors), the tumor had to be analyzed for RNA expression changes between aggressive and nonaggressive cancers. Demonstrating the genomic classifier helps identify men in low and very low categories of risk who have more- or less-aggressive prostate cancer.
“Our study demonstrated that the genome is an independent indicator of more or less aggressive cancer,” explains Dr. Stephenson. “Although it’s not perfect, genomic biomarkers help us distinguish cancer behavior, which influences our decisions regarding surveillance and treatment.”
“When patients hear the word cancer, they often think they need to begin treatment immediately,” notes Dr. Stephenson. “However, many types of prostate cancer don’t behave aggressively and therefore don’t require treatment right away — if at all.”
Advertisement
The study demonstrated that genomic biomarkers lead to a reduction in treatment for low-risk patients who are favorable to surveillance. The study also supports patients and clinicians’ confidence in their decision-making regarding surveillance and treatment.
While Cleveland Clinic researchers have demonstrated the benefits of genomics, they haven’t yet proven that surveying men with low-risk prostate cancer leads to better outcomes. Additional research is needed to assess the long-term impact of using genomic characterization to make decisions regarding surveillance and treatment.
Investigating tissue- and serum-based biomarkers may also lead to stronger tumor characterization and enhanced treatments.
Advertisement
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
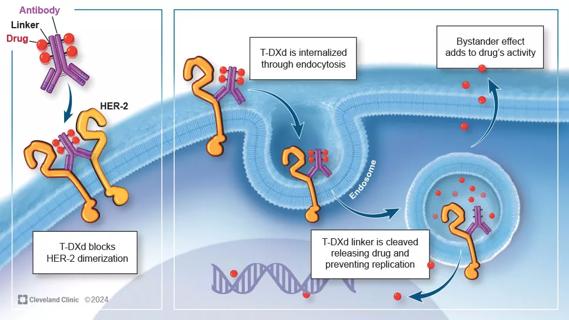
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients