Cleveland Clinic’s radiation oncologists select highlights

The results of hundreds of important studies were presented at the recent 2017 American Society for Radiation Oncology (ASTRO) annual meeting.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Many Cleveland Clinic Cancer Center clinicians and researchers attended and presented at ASTRO’s September 24-27 sessions in San Diego. Since then, we’ve discussed and debated which presentations we found most intriguing or that we feel have the greatest potential to change the practice of radiation oncology.
Here are our top 10:
GOG 249 tested whether adjuvant vaginal cuff brachytherapy followed by VCB/C had superior relapse free survival (RFS) compared to adjuvant pelvic radiation therapy (PXRT). Of 601 patients, acute toxicity was more common and more severe in the VBC/C arm. With a median follow up of 53 months, three-year RFS was 82 percent for both arms. There was no difference in vaginal or distant failure, but pelvic and para-aortic failures were more common in the VCB/C arm. In summary, VCB/C was not superior to PXRT and had more acute and late toxicity. Adjuvant pelvic radiation remains a well-tolerated and efficacious adjuvant treatment for high-risk, early-stage endometrial cancer patients.
RTOG 0915 was a randomized phase 2 trial of lung SBRT for peripheral lung tumors ≤ 5 cm in medically inoperable patients comparing 34 Gy in 1 fraction versus 48 Gy in 4 fractions. With longer term follow up (5.1 years) there was no difference between the two arms with respect to the primary outcome of grade ≥ 3 toxicity, and there was no excess in late-appearing toxicity in either arm. Five-year primary tumor failure, and median OS and DFS were similar in both arms. These long-term results, in conjunction with results from RPCI I 124407 (30 Gy in 1 fraction versus 60 Gy in 3 fractions), have validated single-fraction SBRT as a feasible, trial-based regimen for peripheral stage I NSCLC.
Advertisement
This noninferiority study randomized 820 women with high-risk breast cancer after mastectomy to adjuvant RT with conventional fractionation (50 Gy/25 fx) to the chest wall and regional nodes vs. hypofractionated RT (43.5 Gy/15 fx). The trial was powered to detect a noninferiority difference of 5 percent for five-year locoregional recurrence rate. Median follow up was 52 months. The five-year locoregional recurrence was 6.0 vs. 8.4 percent (P = 0.40) for conventional and hypofractionated RT, respectively. Similarly, five-year OS was 87.1 vs. 84.9 percent (P = SS) for conventional and hypofractionated RT. At five-year follow up, hypofractionated PMRT is not inferior to conventional fractionation PMRT, and its use should be strongly considered.
This trial is a phase 2 randomized study enrolling patients to SBRT plus maintenance chemotherapy, or maintenance chemotherapy alone, with primary endpoint of PFS. Accrual was ended early after an unplanned interim analysis found a significant improvement in PFS from 3.5 to 9.7 months with the addition of SBRT. Toxicity was similar in each arm. This study together with previous data has led to the current phase 3 NRG-LU 002 trial evaluating the addition of SBRT to maintenance chemotherapy on overall survival.
Advertisement
This retrospective comparative outcomes analysis of 1403 patients with Gleason 9-10 (ISUP group 5) prostate cancer treated with RP (N = 639), external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) (N = 734) or EBRT + brachytherapy (BT) (N = 436). Median dose of EBRT (EQD2) was 74 Gy in EBRT group and 91.5 Gy in the EBRT + BT group. On average, androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) was given for 22 months with EBRT and 12 months with EBRT + BT. In both unadjusted and propensity-matched data, EBRT + BT boost (with short-duration ADT) was associated with significantly better disease control compared to RP or EBRT + long-term ADT with respect to distant metastasis free survival (DMFS) and prostate cancer-specific survival (PCSS). No difference was observed between EBRT and RP.
RTOG 0526 evaluated the role of ultrasound guided BT in locally recurrent prostate cancer in patients who received prior EBRT, with a primary endpoint of late GI/GU adverse effects. All patients had biopsy-proven disease, were found to have a local recurrence at least 30 months since initial treatment, and had low or intermediate grade prostate cancer prior to salvage BT. Results showed that the median dose of prior EBRT was 74 Gy, and median time between definitive RT and salvage BT was 85 months. The rate of late-grade 3 GI/GU effects was 14 percent with no grade 4 or 5 late toxicities. The only variable that predicted the severity and timing of late toxicity was higher BT dose. This study demonstrates that full dose BT can be utilized following definitive EBRT with an acceptably low rate of late toxicities.
Advertisement
This analysis focused on the phase 2 group 3 component of this trial that included any WHO grade 3 with gross total resection (GTR) or subtotal resection (STR), recurrent Grade 2 with GTR or STR, or new grade 2 with STR meningioma. Three-year PFS was 59.2 percent; three-year OS was 78.6 percent; and three-year local control was 68.9 percent. The authors concluded that 14 patients progressed, most entirely within the radiation field (13 of 14) with one in-field and marginal (1 of 14). The five-year progression rate was 70 percent for grade 2 compared with 30 percent for grade 3. Adverse events were grade 1-3 except for one grade 5 with radiation necrosis.
This study evaluated the use of ctDNA to evaluate treatment response in patients with stage I-III lung cancer. This study prospectively enrolled 41 patients. ctDNA was collected in all patients prior to definitive treatment as well as post treatment. Median follow-up was 35.1 months. ctDNA detected tumor recurrence prior to CT or clinical recurrence in all patients who recurred, and ctDNA was not detected in patients who did not progress. Two-year OS for patients with positive post-treatment ctDNA was 21.8 versus 94.4 percent when ctDNA was undetectable (P <0.0001). ctDNA also detected disease progression 4.9 months prior to imaging or clinical detection of progression. This study suggests the important role of ctDNA in evaluating response to thoracic RT.
Advertisement
Among patients with stage IIB disease, neither BT dosing nor the addition of chemotherapy had a significant influence on OS. This result provides guidance to those treating women with cervical cancer, and the study also demonstrates the feasibility of conducting global clinical trials, including trials in lower- and middle-income countries where resources for research tend to be more restricted.
This study examined outcomes in 1566 patients with pT3 disease or positive margins noted on prostatectomy who underwent either postprostatectomy adjuvant RT or surveillance followed by early salvage RT at the time of biochemical recurrence. There was no difference in OS or DMFS at 10 years. However, PCCS (99 vs 97 percent) and 10-year freedom from biochemical failure (75 vs 59 percent) were improved with the use of adjuvant RT. On multivariate analysis, adjuvant RT was significantly associated with decreased risk of biochemical failure. These findings represent the largest available data set to compare the outcomes of adjuvant versus early salvage RT after prostatectomy.
Advertisement

First-of-its-kind research investigates the viability of standard screening to reduce the burden of late-stage cancer diagnoses

Global R&D efforts expanding first-line and relapse therapy options for patients
Study demonstrates ability to reduce patients’ reliance on phlebotomies to stabilize hematocrit levels

A case study on the value of access to novel therapies through clinical trials

Findings highlight an association between obesity and an increased incidence of moderate-severe disease
Cleveland Clinic Cancer Institute takes multi-faceted approach to increasing clinical trial access 23456
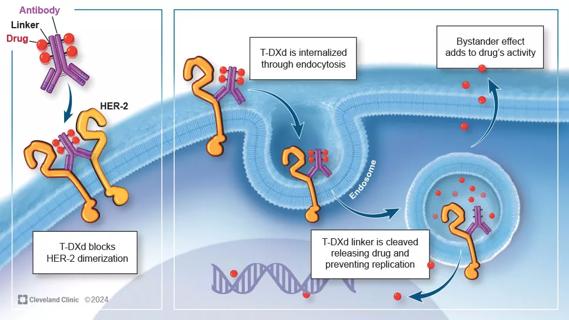
Key learnings from DESTINY trials

Overall survival in patients treated since 2008 is nearly 20% higher than in earlier patients