A quick look at this increasingly common condition
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an inflammation of the esophagus caused by an overabundance of eosinophils and is a disease that is being more frequently diagnosed. It can affect 1 in 10,000 pediatric patients, and typically affects adolescent Caucasian males in 95 percent of cases. Symptoms include frequent and recurrent esophageal dysphagia and food impaction complaint and can also include gastroesophageal reflux symptoms that are refractory to therapy. Children can develop feeding disorders that can lead to inhibited growth.



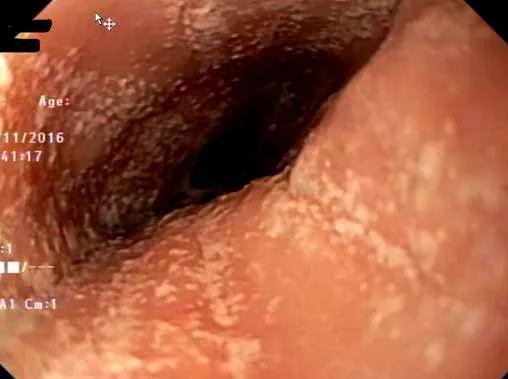
EoE is a disease that is diagnosed primarily via histologic findings. On upper endoscopy, the patients will have characteristic esophageal findings, which include linear furrows or rings, esophageal plaques, and in severe cases, esophageal strictures. On pathologic examination, patients will have greater than 15 eosinophils per high powered field, especially in the upper esophagus.

White plaques in esophagus
Patients commonly present to pediatric gastroenterology with symptoms of dysphagia, or in the acute setting, after sustaining a food impaction. This typically requires endoscopic removal and frequently the visual findings of EoE are seen during the endoscopic removal.
Recent years have seen improvements in diagnostic, monitoring and treatment approaches, including breakthroughs in biologic therapies and promising blood and urine biomarkers. A new tool for assessing severity called the Index of Severity for EoE (I-SEE) is available. The tool has three domains: symptoms and complications, inflammatory features and fibrostenotic features and is useful in both adult and pediatric patients. It is intended to help guide conversations between clinicians and pathologists as to the most relevant features for measuring EoE severity for each individual patient.
Advertisement
Dr. Patel is fellowship program director and staff in the Department of Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition in the Digestive Disease & Surgery Institute.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Systemic change needed to improve health outcomes for parents and children, say researchers
Rare genetic variant protected siblings against seizures and severe hypoglycemia

Movie has more positive impact than expected, says Head of Adolescent Medicine

Genetic changes are similar between some vascular anomalies and cancers
Expert panel advises a two-tier structure for surgical centers
Our new head of pediatric general and thoracic surgery shares his passion and vision
Basic understanding of condition and treatment is lacking