Olman lab offers new insights for treating IPF
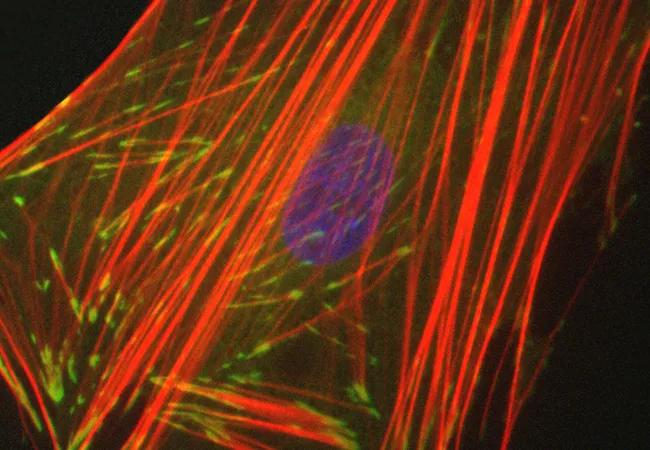
Fibrotic disorders such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) result in progressive scarring and organ dysfunction. In IPF, persistent activation and accumulation of fibroblasts results in excessive connective tissue accumulation and tissue contraction that makes the lung increasingly “stiffer.” This increased tissue stiffness serves as a signal for recruitment and activation of more fibroblasts in a feed-forward fashion that perpetuates the fibroproliferative cycle.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Two recent studies from the lab of Dr. Mitchell Olman and colleagues at Cleveland Clinic’s Lerner Research Institute offer glimpses into this cycle that may one day produce novel therapeutic agents for patients with IPF.
Much of the research on fibroblast activation in IPF has been performed using plastic or glass tissue culture assay systems that are 1 million orders of magnitude stiffer than actual lung tissue, and may not provide an accurate representation of in vivo fibroblast behavior. In work recently published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry, Dr. Olman and colleagues characterize a novel assay system that more closely mimics the natural lung environment of the fibroblast by using actual normal and fibrotic lung tissue. With this system, they identified for the first time that normal lung stimulates migration of fibroblasts, while fibrotic lung stimulates myofibroblast differentiation. They also demonstrated how these two different responses (migration and myofibroblast differentiation) are both mediated through the molecular motor myosin II. Depending on whether the fibroblast interacts with normal or fibrotic lung, myosin II is activated in a way that either results in migration or myofibroblast differentiation.
The multiple redundant and overlapping pathways in fibrotic disease have been well established. A heterogeneous population of patients suffer from IPF, and ample evidence demonstrates that the mechanisms underlying the development of fibrosis may vary between patients.
Advertisement
One of the biggest disappointments in the field of IPF has been the number of clinical trials demonstrating either no efficacy or actual harm with the investigated therapies. Many of these trials tended to focus on individual soluble mediators or isolated pathways known to play a role in fibrosis. Identifying a potential therapeutic strategy that targets a molecule, such as myosin II, that is downstream and common to multiple fibrosis pathways, could represent a significant paradigm shift in the treatment of patients with IPF and other fibrotic disorders.
The Olman lab has also published exciting new research demonstrating for the first time that the mechanosensing signal in fibroblasts is mediated by the transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 (TRPV4) channel. In this work, they demonstrated that the TRPV4 signal converges on this same myosin II protein in fibroblasts.
Together, these studies suggest that the fibroblast senses increases in tissue stiffness through TRPV4 and translates those increases into the activation of myosin II in a way that creates a “pro-fibrotic” fibroblast. Future work will explore the possibility of a dysregulated myosin II pathway in fibroblasts from IPF patients, and whether manipulation of this fibrotic lung-driven pathway could lead to novel therapeutic agents for the devastating disorder of IPF.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Volatile organic compounds have potential in heart failure diagnostics

Caregivers are provided with real-time bronchoscopy patient findings
Insights for diagnosing, assessing and treating
A Cleveland Clinic pulmonologist highlights several factors to be aware of when treating patients

New program sets out to better support underserved patient populations
Cleveland Clinic pulmonologists aim to further lower waitlist times and patient mortality

Lessons learned from cohorting patients and standardizing care
New tools and protocols to improve care