An overview of case reports and management
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Nonthrombotic pulmonary embolism (NTPE) is uncommon and can be difficult to diagnose. My colleagues and I recently reviewed this complete or partial occlusion of the pulmonary vasculature resulting from inorganic particulate matter and foreign bodies in Chest. The below images demonstrate accidental embolization from ethiodized oil and silicone.
Ethiodized oil is used to visualize the lymphatic system in cases of thoracic duct leakage/injury. Image A, a postero-anterior chest radiograph, and image B, a lateral radiograph, demonstrate the oil in the distribution of the right lower lobe (red arrows). Yellow arrows indicate the metallic embolization coils used to treat the leakage site.
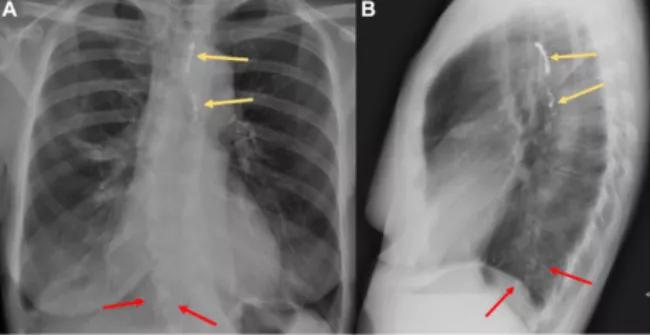
Extravasion leading to embolization to the pulmonary or cerebral vasculature is a complication of the procedure, and symptoms increase with the volume of oil used. Ethiodized oil embolization may present with hypoxia and show as pulmonary infiltrates on standard chest radiographs (CXRs). A noncontrast CT may show accumulation of oil-like high-density materials and diffusely increased attenuation with interstitial thickening in the lungs.
Unfortunately, there is no definitive therapy for this complication. Supportive care and low-molecular-weight heparin can be beneficial.
Many pulmonary complications of subcutaneous cosmetic silicone injections have been reported, from alveolar hemorrhage to death. Patients with silicone embolism syndrome typically present with fever, cough, hypoxia, altered mental status and chest pain within a few minutes of injection. A CSX may show diffuse patchy alveolar infiltrates (acute) and hilar adenopathy and increased interstitial markings (chronic).
Advertisement
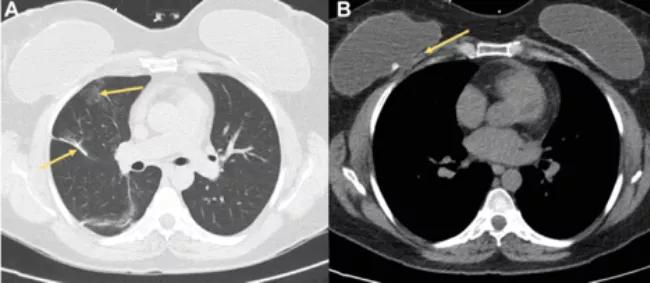
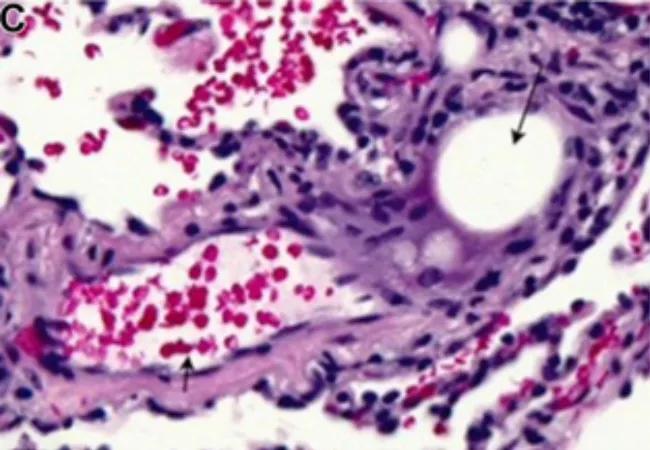
On noncontrast CT (lung window), you may observe ground glass opacities (as seen in image A, upper right lobe) and interlobular septal thickening similar to what you might see in fat embolism. Image B shows changes in the fat plane between the pectoralis and the posterior capsule of a right breast implant. Silicone embolization from breast augmentation is quite rare, and pathology in these cases show silicone globules (long arrow) in or next to the pulmonary microvasculature (short arrow).
Supportive management remains key, from endotracheal intubation for respiratory failure to venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and plasmaphresis for refractory hypoxemia.
These are rare occurrences, and patients may present with a wide spectrum of signs and symptoms from none to severe. Accurate diagnosis requires extensive knowledge of imaging modalities and post-processing tools. Other posts review macroscopic emboli like catheter tips and guidewires, polymethylmethacrylate cement and brachytherapy seeds and talc granulomatosis.
Cleveland Clinic coauthors include Sanjay Mukhopadhyay, MD, staff, Department of Anatomic Pathology, Derick Asah, DO, resident, and Subha Ghosh, MD, staff, Department of Diagnostic Radiology.
Dr. Mehta is staff in the Department of Pulmonary Medicine.
Images and text republished with permissions from Elsevier. Originally published in Chest.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Volatile organic compounds have potential in heart failure diagnostics

Caregivers are provided with real-time bronchoscopy patient findings
Insights for diagnosing, assessing and treating
A Cleveland Clinic pulmonologist highlights several factors to be aware of when treating patients

New program sets out to better support underserved patient populations
Cleveland Clinic pulmonologists aim to further lower waitlist times and patient mortality

Lessons learned from cohorting patients and standardizing care
New tools and protocols to improve care