Centralized management yields favorable results
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/c7a7115c-0d2e-4778-8514-a28917ae9628/17-PUL-3670-Mazzone-Hero-Image-650x450pxl_jpg)
17-PUL-3670-Mazzone-Hero-Image-650x450pxl
By Humberto Choi, MD, and Peter Mazzone, MD, MPH
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The Center for Medicaid and Medicare Services (CMS) and U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommend lung cancer screening with a low-dose chest CT scan (LDCT) for a well-defined cohort at high risk of having lung cancer based on age and smoking history. Our years of experience in designing, implementing, testing and improving Cleveland Clinic’s lung cancer screening program have conferred valuable insights from which other programs may benefit.
Lung cancer screening reduces lung cancer mortality, but this benefit is only realized in a small fraction of screened patients. Harms of screening include the performance of the test (radiation exposure) and the evaluation of screen-detected findings (anxiety, morbidity and mortality from procedures). Most stakeholder societies feel the balance of benefit and harms favors lung cancer screening while also recognizing that this favorable balance depends upon screening in high quality programs.
Important aspects of screening, capable of altering this balance, include the selection of screen-eligible patients, appropriate management of screen-detected findings and smoking cessation. Given the potential for harm, it is also important that patients are educated in a manner that allows them to make value-based decisions about participation.
We implemented Cleveland Clinic’s lung cancer screening program in 2012. Our multidisciplinary program is structured to meet the core components of a high quality screening program outlined by the American Thoracic Society and American College of Chest Physicians. Our program uses clinical care paths that guide the management of common incidental findings such as coronary artery calcification and thyroid nodules. These care paths are based on specialist expertise and national guidelines.
Advertisement
Initially, a provider ordering a LDCT was responsible for communicating with the patient and managing the screening results. Based on a review of screening performance and mandates for both the provision of a shared decision-making visit and data reporting to a national registry, we centralized communication and management within the lung cancer screening program in April 2015. Now, rather than ordering the screening itself, providers instead order a consult to the screening program.
Following centralization, the number of patients screened who were outside the CMS criteria decreased, and the percentage of screen-detected Stage I cancers increased. These findings suggest to us the value of the centralized approach to screening in our health system.
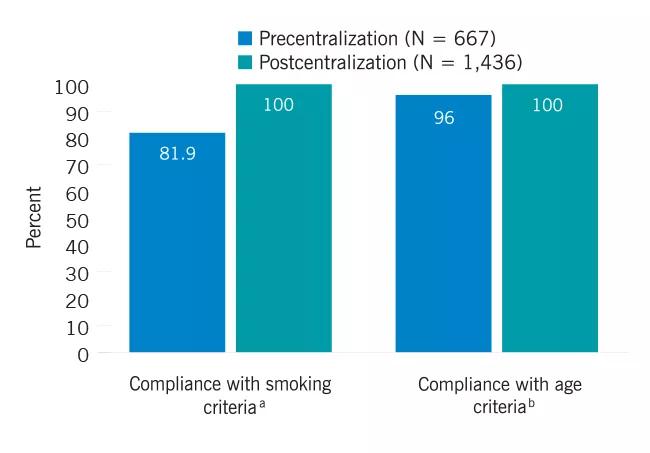
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/eb813c12-b119-4788-a8a6-b9ab795906a3/17-PUL-3670-Mazzone-Inset-Graph-01-650pxl-width_jpg)
Improvement in compliance with screening guidelines following centralization (N = 2103), 2012-2017. a Eligible smoking criteria is ≥ 30 pack years and are current smokers or have quit smoking in last 15 years. b Eligible age range for LDCT screening is 55-77.
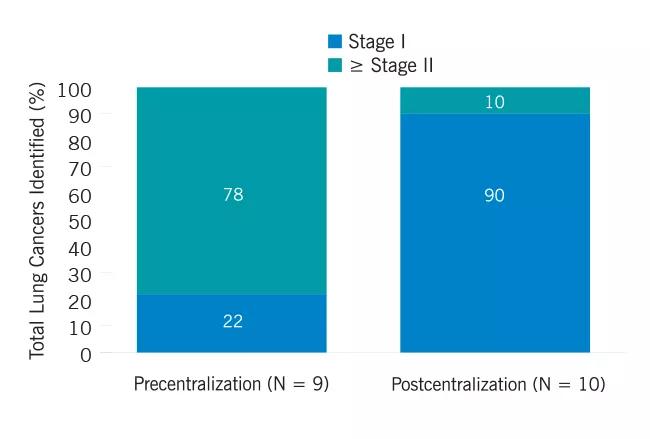
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/43cd81e9-8426-493e-9ea2-8f11f5d146c1/17-PUL-3670-Mazzone-Inset-Graph-02-650pxl-width_jpg)
Early-stage cancers diagnosed as a percentage of the total lung cancers identified (N = 19), 2012-2017.
Based on our experience at Cleveland Clinic, we favor centralized management of screening decisions in our health system, detailed and thorough shared decision-making visits with one-year follow up (see our previous article here), and concrete plans for managing incidental findings (and here).
We continue to conduct research to provide evidence-based support for the elements of a quality program. Currently, we are reviewing reasons why some eligible patients choose not to enter our screening program, why others are noncompliant with their annual visit, and whether the shared decision-making visit impacts rates of smoking cessation. We hope these results will translate into further improvements to our program.
Advertisement
Dr. Choi is staff in the Respiratory Institute. Dr. Mazzone is Director of the Lung Cancer Program and Lung Cancer Screening Program for the Respiratory Institute.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Volatile organic compounds have potential in heart failure diagnostics
Caregivers are provided with real-time bronchoscopy patient findings
Insights for diagnosing, assessing and treating
A Cleveland Clinic pulmonologist highlights several factors to be aware of when treating patients
New program sets out to better support underserved patient populations
Cleveland Clinic pulmonologists aim to further lower waitlist times and patient mortality
Lessons learned from cohorting patients and standardizing care
New tools and protocols to improve care