Recurrence warrants nephrology or urology specialist
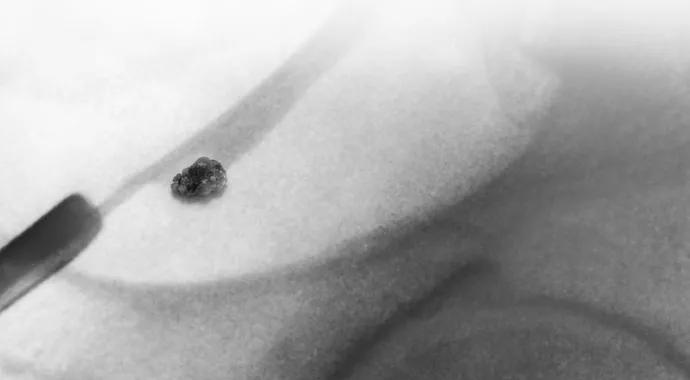
Most patients suffering from a kidney stone attack visit their primary care physician (PCP) or the emergency department for immediate treatment of the pain. While preventive efforts to decrease the risk for future attacks is a good first step, many patients may benefit from seeing a specialist to determine both the cause of their stones and proper therapies.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Since kidney stones are very common and widespread in the general population, most of those patients are seen by their PCPs,” says Cleveland Clinic nephrologist Juan Calle, MD.
“General instructions about diet and fluid intake for prevention of kidney stones are often sufficient if a patient has had only one stone formed (depending on the size and any associated comorbidities) with no complications.”
However, more than 40 to 50 percent of patients will have a recurrence of the disease within five years. For that reason, Dr. Calle says, this patient population would potentially benefit from seeing a specialist (either nephrology or urology) at least once.
A urologist and/or nephrologist will determine the exact cause of the kidney stones. Because there are several types of kidney stones and the causes for each vary, knowing this information is critical in determining the best course of treatment and prevention, including medical management of the condition on an ongoing basis.
“Our work as nephrologists is mainly to focus on prevention of the stone and to make sure no other associated diseases are the cause for them or a worsening factor,” Dr. Calle explains. “I believe almost all patients with multiple kidney stones or large kidney stones and associated diseases should have a referral to nephrology for prevention and management of those associated conditions.”
Typically, a urologist or nephrologist will conduct some sort of imaging during the appointment, whether that be a CT scan, X-ray or ultrasound.
Advertisement
Typically, Dr. Calle says, there should be a urine analysis and basic blood work. In cases involving more than one kidney stone or when other associated diseases are possible causes, a 24-hour urine collection may provide useful information.
“While the main focus is on diet and fluids, there are some conditions that require special treatments to handle the risk factors that promote the formation of kidney stones,” Dr. Calle adds. “Most definitely, patients who may have genetic abnormalities causing the stones should be treated by a specialist in the area.”
Once the cause and type have been determined, there are now highly successful minimally invasive treatments, Dr. Calle says.
At Cleveland Clinic’s Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute, most patients with stones have the potential to be seen by either specialist (preferably urology in the acute setting or nephrology to begin the workup). Treatment options include ureteroscopy, shock wave lithotripsy (SWL), SWL under conscious sedation and percutaneous nephrolithotomy.
These and other solutions are available to relieve your patients’ kidney stones and return them — pain-free — to your care.
Advertisement
Advertisement
OMT may be right for some with Graves’ eye disease
Perserverance may depend on several specifics, including medication type, insurance coverage and medium-term weight loss

Integrate climate-related health information and counseling into your practice
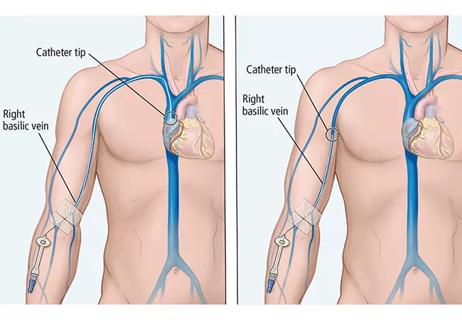
Physicians discuss a specific case example, and PICC pros, cons and alternatives

A snapshot of the 2020 GINA report

A review of available interventions
Abstinence from combustibles, dependence on vaping
An historical view of the disease