Experienced team, innovative treatment
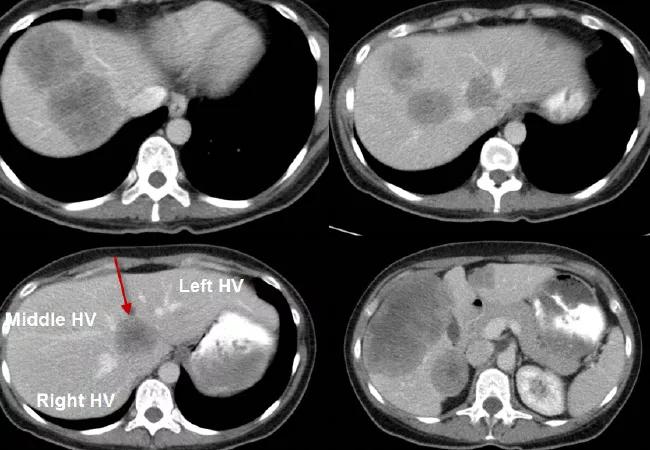
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/90ebbb11-aed8-4e27-91f8-ddfcdca03dd1/17-DDI-3877-Quintini-CQD-Hero_jpg)
17-DDI-3877-Quintini-CQD-Hero
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 42-year-old female was referred to our institution with large right colon cancer and synchronous bilobar liver metastasis (see presenting CT scan of the liver above). A particular challenge was presented by the lesion encasing the three hepatic veins of the liver (see arrows).
The patient received three months of perioperative chemotherapy and was scheduled (three months after the initial presentation) for a two-stage hepatectomy and a combined resection of the primary right colon tumor.
The first surgery included a right hemicolectomy with resection of all the left-sided liver lesions. The surgery was uneventful. On postoperative day 6, the patient underwent a right portal vein embolization with the intent to induce hypotrophy of the right hemi liver and the hypertrophy of the left hemi liver. This approach is used to decrease the risks of postresection liver failure.
Six weeks after the first operation, the patient underwent a right hepatectomy. Given her young age and the extent of the disease, the decision was made to place to also place a hepatic artery infusion (HAI) pump to further decrease her likelihood of recurrence. HAI locoregional treatment is an innovative approach that improves survival after liver resection for metastatic colon cancer. This treatment option is only delivered in selected centers around the world.
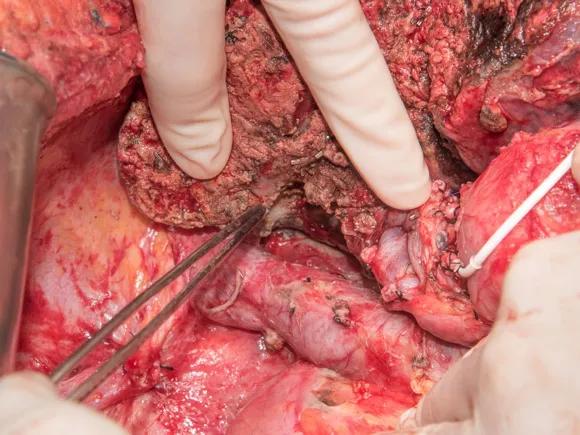
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/336ab2a6-d780-428c-bfa0-43a6027e8fe5/17-DDI-3877-Quintini-CQD-Inset1_jpg)
The remnant left liver lobe with a catheter inside the gastro-duodenal artery for HAI treatment.
One year after the initial presentation, the patient is free of tumor (see scan below) and receiving routine follow-up scans.
Advertisement
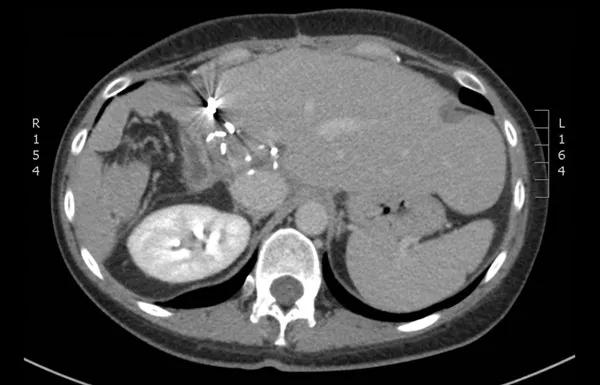
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/375db05f-5da2-45c9-9963-5600dbbcf5ee/17-DDI-3877-Quintini-CQD-Inset2_jpg)
CT scan showing the patient free of tumor.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Strong patient communication can help clinicians choose the best treatment option
ctDNA should be incorporated into care to help stratify risk pre-operatively and for post-operative surveillance
The importance of raising awareness and taking steps to mitigate these occurrences
New research indicates feasibility and helps identify which patients could benefit
Treating a patient after a complicated hernia repair led to surgical complications and chronic pain
Standardized and collaborative care improves liver transplantations
Fewer incisions and more control for surgeons
Caregiver collaboration and patient education remain critical