Residual dissection requires lifelong surveillance
By Cassandra Beck, DO, and Francis Caputo, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Open proximal aortic repair remains the standard of care for treatment of acute type A aortic dissection (ATAAD). Even when repair is successful, the distal false lumen may remain patent and lead to progressive aneurysmal degeneration of the involved residual aorta. Patients with residual dissection following type A repair often undergo multiple reoperations for disease progression. Chronic post-dissection thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysms (TAAAs) present significant therapeutic challenges due to the significant morbidity and mortality associated with repair.
Patients can be treated with open surgical, endovascular or hybrid techniques, depending on the complexity of the anatomy, patient factors and operator experience. Cleveland Clinic’s Aorta Center has become a national and international referral center for patients requiring complex aortic repairs such as the one profiled below, which ultimately represented total aortic replacement.
A 58-year-old woman with a past medical history of acute repair of type A aortic dissection presented for a surveillance CT angiogram. Her initial repair was done at age 43 at an outside institution, and at age 55 she further required a staged arch and TAAA open repair, which was performed by a cardiothoracic surgery team in Cleveland Clinic’s Aorta Center.
CT angiogram at her current presentation demonstrated progressive aneurysmal degeneration of the chronically dissected untreated segments of the infrarenal aorta and bilateral common iliac arteries (Figure 1). She was referred for evaluation by Aorta Center vascular surgery staff, who recommended open aortoiliac repair.
Advertisement
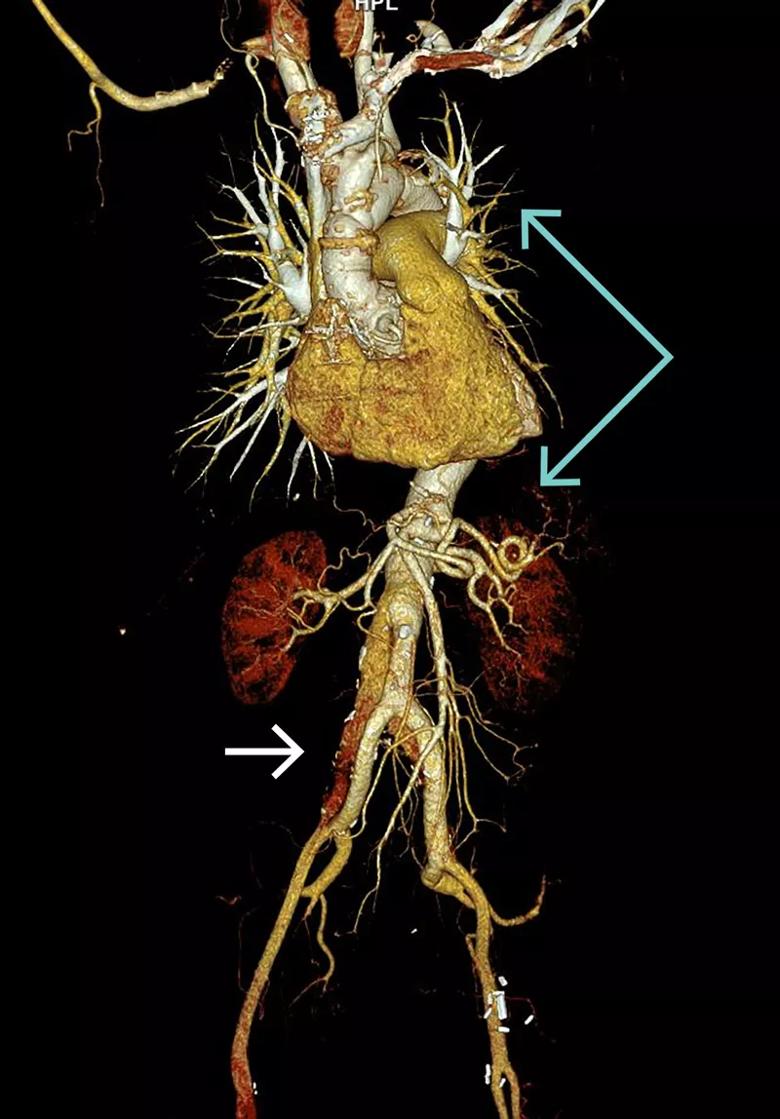
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/e5200349-eefa-4f22-aa72-ddbb17d49a48/19-HRT-3946-Caputo-Beck-Inset-1-CQD_jpg)
Figure 1. Volume-rendered three-dimensional CT reconstruction of contrast-enhanced images demonstrating intact surgical repair of the ascending aorta, aortic arch and thoracoabdominal aorta to the level of the renal arteries (blue arrows) and residual chronic dissection with aneurysmal degeneration of the infrarenal aorta and bilateral common iliac arteries (white arrow).
The patient underwent a final open infrarenal aortic repair with bypass to the right internal and external iliac arteries and to the left common iliac artery bifurcation (Figure 2). She recovered without complications and neurologically intact.
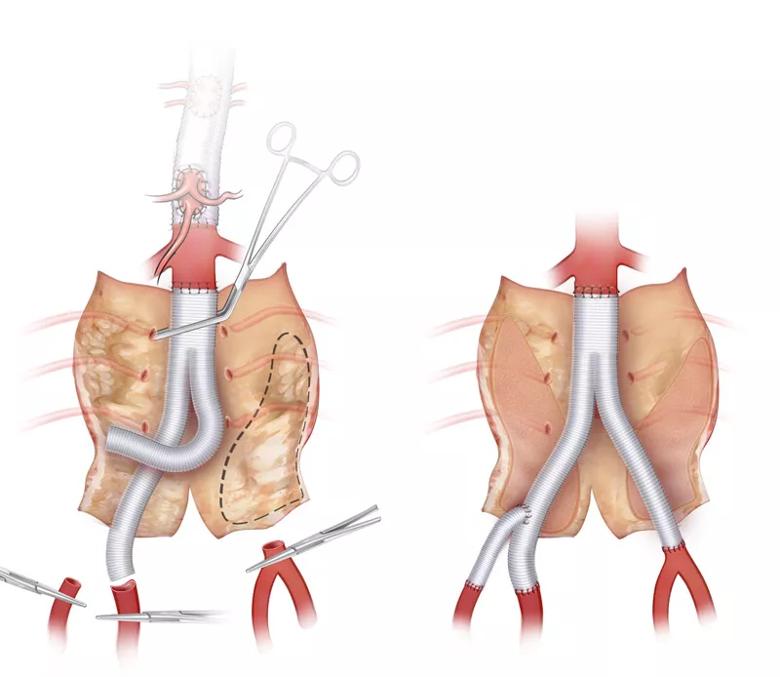
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/a7bb320f-7182-4daf-9c62-5ed861f88265/19-HRT-3946-Caputo-Beck-Inset-2-CQD_jpg)
Figure 2. Illustration demonstrating open repair of the infrarenal aorta with resection of the intimal flap and bypass to the right internal and external arteries and left common iliac artery bifurcation.
We have described a case of multidisciplinary, multistage open total aortic replacement for aneurysmal degeneration of the residual chronically dissected thoracoabdominal aorta and bilateral common iliac arteries after emergency repair of ATAAD more than a decade earlier. This case highlights the following important points:
Advertisement
Dr. Beck is a fourth-year resident and Dr. Caputo is a vascular surgeon in Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Vascular Surgery.
Advertisement
Advertisement
A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery
Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation
Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable