Cleveland Clinic launches global BlueSync Field Evaluation

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/4391ef92-2592-40b7-8d41-814253587e11/18-HRT-4823-BlueSync-CQD-Hero-2_jpg)
18-HRT-4823-BlueSync-CQD-Hero-2
In early July, a Cleveland Clinic patient became the first in the U.S. to use their smartphone to directly monitor their implanted cardiac pacemaker. The patient was enrolled in a multicenter international study with the potential to reshape remote monitoring of patients with pacemakers.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The 12-month study (NCT03518658) is evaluating patient and clinician perceptions of Medtronic’s BlueSync™ technology, which for the first time allows automatic, wireless remote monitoring of a pacemaker directly using the patient’s smartphone or tablet. When paired with a compatible smartphone app, BlueSync-enabled devices communicate through Bluetooth® wireless telemetry to the Medtronic CareLink™ cellular network to allow clinicians to remotely review alerts of patient events at any time and remotely check their devices periodically.
Some 252 patients with bradycardia who are implanted with cardiac pacemakers (including cardiac resynchronization therapy [CRT] pacemakers) will be enrolled in the Medtronic-sponsored study, whose goal is to assess patients’ feedback and measure compliance with prescheduled remote transmission of their device data.
“Evidence is abundant that remote monitoring of cardiac implanted devices improves outcomes, but despite ample supportive evidence and evolutions in technology, the compliance level has been disappointing,” says global principal investigator Khaldoun Tarakji, MD, MPH, Director of Outpatient Electrophysiology and Remote Monitoring at Cleveland Clinic. “Up to now, fewer than half of patients with remote monitoring-capable devices actually use the feature.”
In the early days of implanted CRT devices, patients made frequent visits to the clinic, where physicians would physically interrogate their devices. Next came early home-based devices that allowed for transmission via landlines, then wireless monitoring via cellular networks.
Advertisement
Today, most remote monitoring is still carried out using a physical box in the patient’s home, which picks up prescheduled or event-triggered signals from the patient’s implanted device when it is nearby and transmits them to the cellular network.
But some patients find the devices daunting and give up if they have trouble setting up the system at home. Even when the system is functioning properly, the transmission process remains invisible to the patient. “With these systems, patients send transmissions just by being near the box in their bedroom, but they don’t see anything,” Dr. Tarakji explains. “They tell me they don’t know whether or not I’m getting their data. The lack of feedback is a major issue.”
And if a prescheduled transmission doesn’t take place, a nurse has to call the patient. “So you have this 2018 technology, but the troubleshooting is still back in the 1970s or ’80s,” he observes.
The BlueSync system for the first time makes it possible for patients implanted with compatible devices — thus far only certain pacemakers or biventricular pacemakers, not defibrillators — to send transmissions without being near a box or even at home. They just need to have an iOS smartphone or tablet with Bluetooth turned on. (The technology will be available for Android devices in the near future, Dr. Tarakji notes.)
With Medtronic’s MyCareLink Heart™ app downloaded on their phones, patients now see a check mark following a successful transmission. The app (see photo) also includes pages for recording symptoms and tracking vital signs or physical activity, as well as information on battery life, transmission schedules, educational material about pacemakers, and even their clinic’s address and phone number.
Advertisement
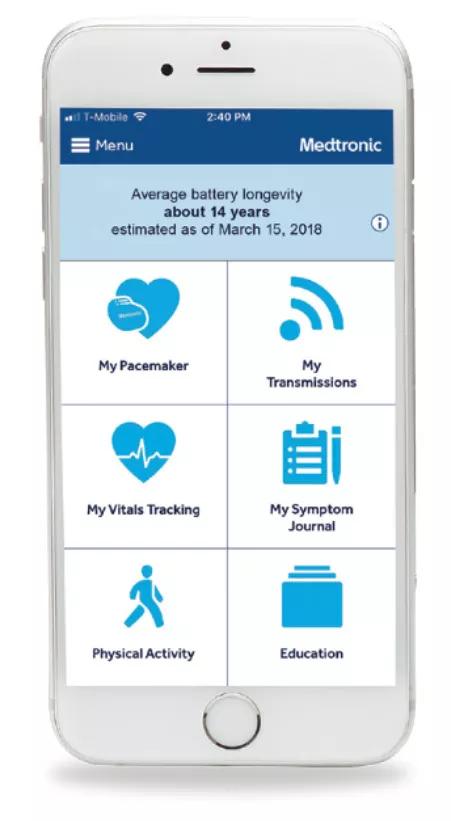
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/0b1b5175-f29e-447c-8004-6f09a075c6a5/18-HRT-4823-BlueSync-CQD-Inset_jpg)
A glimpse of the MyCareLink Heart app. Photo courtesy of Medtronic.
No pacemaker data are stored in the phone, which serves merely as a vehicle for transmitting data via Wi-Fi or cellular network.
Patients still need to visit the clinic about once a year since not everything can be checked remotely and because settings can’t be changed remotely, for security reasons. Still, Dr. Tarakji believes the BlueSync model is leaps and bounds ahead of prior systems, which he hopes the newly launched BlueSync study will demonstrate.
The study’s primary objective is to assess compliance by examining the percentage of quarterly scheduled transmissions completed within a prescribed time window over a 12-month period. Secondary outcomes include patient adoption of remote monitoring as well as patient and provider experience with the BlueSync system.
Patients will be asked questions such as how much control they feel they have over their heart condition when using the system. “We want to address issues of satisfaction and anxiety,” Dr. Tarakji notes. “Is this making patients more stressed out, or is being able to see their data giving them relief and reassurance?”
Patients and clinic nurses will be asked to rate their experiences with the device-pairing procedure. “We will also get feedback from clinic nurses who activate and pair a patient’s device with the smartphone, to gauge their level of comfort with the technology,” Dr. Tarakji says.
Notably, patients who are offered remote monitoring but turn it down will be asked why.
Advertisement
The hope is that the study will inform future iterations of the technology, starting with software tweaks and eventually evolving into next-generation hardware. “If we see better compliance with this new monitoring modality, it will push the field forward,” Dr. Tarakji predicts.
Photo at top used courtesy of Medtronic.
Advertisement
Advertisement
A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery
Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation
Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable