Putting an emerging tool in clinical context
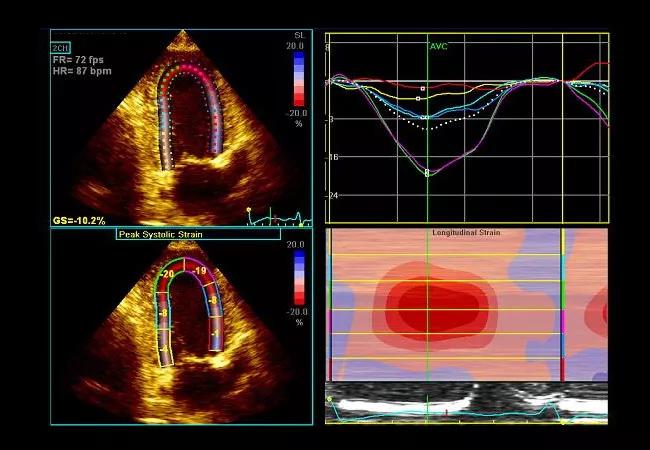
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/ee271adc-a1da-4522-a9f8-6589dfeff001/17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-hero_jpg)
17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-hero
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 71-year-old man presented with progressive and profound fatigue, weight loss and palpitation. His past medical history was notable for bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome 10 years earlier. Electrocardiogram showed low voltage in the limb leads, poor R wave progression and atrial fibrillation. Echocardiogram showed severe increased wall thickness (image below).
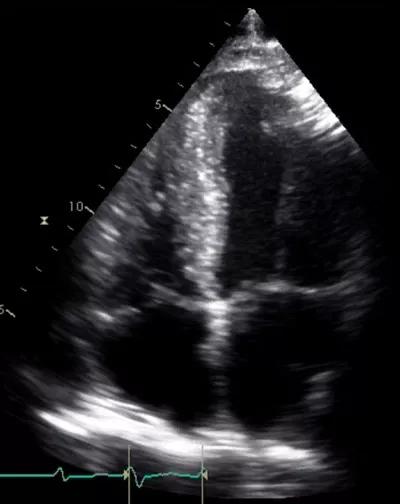
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/67cdec7a-b318-44aa-a697-ad31dcec27e8/17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-F1_jpg)
Although ejection fraction (EF) was preserved, longitudinal function by tissue Doppler was markedly reduced (image below).
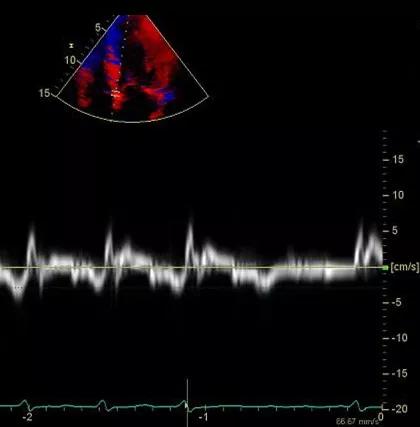
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/13c1951a-1e32-4ba0-a45d-31399605a587/17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-F2_jpg)
As shown in the image below, longitudinal strain demonstrated a distinctive apical sparing pattern.
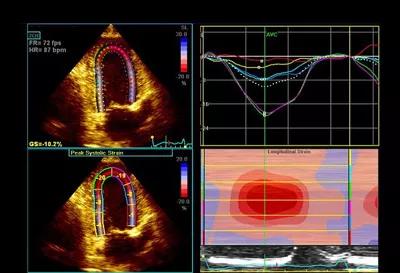
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/d715e1a8-6046-4653-a4ec-8549f1d78e90/17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-F3_jpg)
The sum of apical segmental strain values was greater than the sum of mid and basal segmental strain values in the “bull’s eye” strain plot (image below), a finding that has been shown to be sensitive and specific for cardiac amyloidosis.
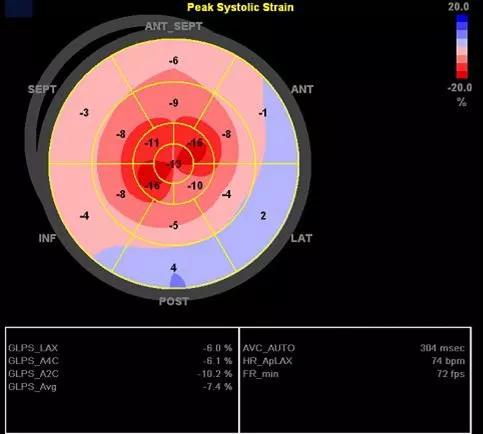
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/cf892407-bb0c-4873-a186-0fe91304b68c/17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-F4_jpg)
The patient went on to have a positive technetium pyrophosphate cardiac scan with SPECT CT, which revealed diffuse myocardial uptake suggestive of ATTR amyloid (image below). Genetic testing identified a specific TTR mutation, and the patient was started on medical therapy and referred for liver transplant evaluation.
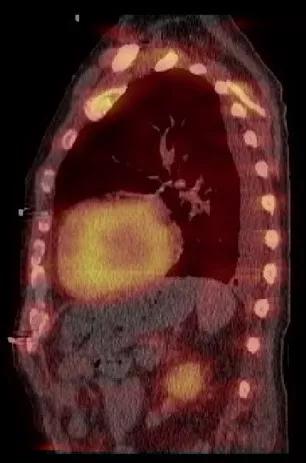
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/f036aea6-5947-4be5-9089-16525d795b21/17-HRT-3429-Collier-Speckle-CQD-F5_jpg)
In terms of clinical utility, speckle-tracking echocardiography has arguably had the most diagnostic and prognostic success when applied to cases of undifferentiated left ventricular hypertrophy — not just as a means of identifying systolic dysfunction in the context of normal EF but also for aiding diagnosis of rarer causes of left ventricular hypertrophy. These include hypertrophic cardiomyopathy or, as in this case, cardiac amyloidosis. The earlier a diagnosis can be made, the sooner definitive therapies can be considered.
Advertisement
At Cleveland Clinic, we recommend assessing global longitudinal strain in all patients with undifferentiated left ventricular hypertrophy and calculating the relative regional strain ratio, as above, in those who have a visual pattern suggestive of cardiac amyloidosis.
Undifferentiated left ventricular hypertrophy is one of several clinical applications of speckle-tracking echo explored in a featured review I published with Cleveland Clinic colleagues in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) earlier this year (2017;69:1043-1056). As we discuss there, speckle-tracking echo appears to be here to stay. While the technique holds much potential, we argue that physicians are well-advised to recognize its technical challenges and limitations before applying speckle tracking and similar strain-based imaging techniques in clinical contexts. Click here for a link to the JACC review.
Dr. Collier (colliep@ccf.org) is a cardiologist in the Section of Cardiovascular Imaging in Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Cardiovascular Medicine.
Advertisement
Advertisement
A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery
Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation
Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable