In very large prostates, robot offers significant advantages
By Jaya Sai Chavali, MD; Juan Garisto, MD; and Jihad Kaouk, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In this video case study, we demonstrate our step-by-step simplified robot-assisted prostatectomy technique to successfully treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Of particular note, the robotic approach offers excellent visualization of the surgical field, decreases blood loss and most important, speeds healing, even in cases like this one with a large (100+ cc) prostate. Rapid healing is due to our added ability to advance the mucosa over the excision site to eliminate raw surface at the excision bed.
A 73-year-old man with a history of lower urinary tract symptoms presented to our practice with an International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) of 22 and urinary retention. Preoperative assessment included a cystoscopy that demonstrated a bilobar obstructing prostate (estimated prostate volume of 400cc) and normal urothelial lining. His PSA was 2.2. Due to failed medical therapy and the severity of the gentleman’s complaints, we elected to perform robot-assisted simple prostatectomy.
We have refined a simplified robot-assisted prostatectomy technique that provides excellent visualization. Major steps in this robotic procedure:
Advertisement
Total operative time was 186 minutes with an estimated blood loss of 200 ml. Pathology reported BPH with a prostate volume of ±300 cc. There were no intraoperative complications.
The patient was discharged on postoperative day one. A cystogram performed two weeks after surgery showed a dye-filling defect contained in the prostatic capsule area and no extravasation. The vesicourethral junction was intact after the removal of the adenoma.
Our simplified robot-assisted prostatectomy procedure, simple to perform by experienced surgeons, offers distinct advantages particularly for patients with large prostate volumes.
Drs. Chavali and Garisto are clinical fellows at the Glickman Urological & Kidney Institute.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Clinicians should individualize dosing practices based on patient risk factors and preferences
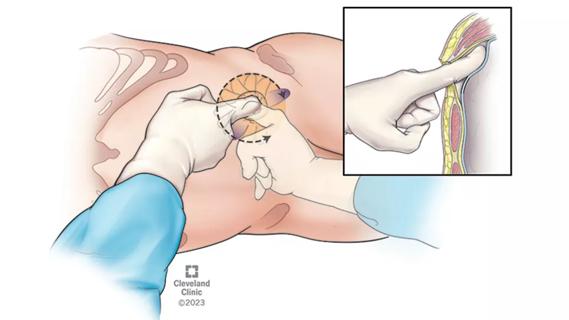
Pioneering and refining the approach in pyeloplasty, nephrectomy and more
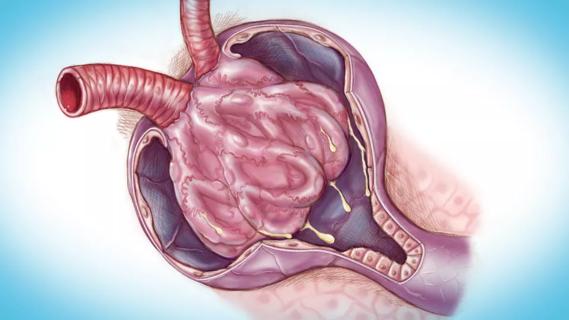
Fully-automated process uses preop CT, baseline GFR to estimate post-nephrectomy renal function
Could mean earlier treatment, but also could have negative effects

Unlike earlier pills, new drugs do not cause liver toxicity

Male factors play a role in about half of all infertility cases, yet men often are not evaluated
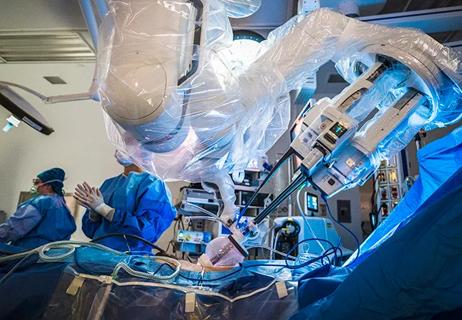
Surgeons choreograph nearly simultaneous procedures, sharing one robot between two patients

Identifying barriers in the renal genetic assessment of Black patients