Surprisingly, biggest effect seen in patients with preserved LVEF
Prescribing a renin-angiotensin system (RAS) inhibitor at hospital discharge following transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is associated with significant reductions in death and in hospitalization for heart failure one year after the procedure. That’s the finding of a large registry-based retrospective cohort study recently published in JAMA (2018;320:2231-2241).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The study, which confirms prior observational studies suggesting a prognostic benefit from RAS inhibition in patients with aortic stenosis, is the strongest evidence of such benefit to date, says co-author Samir Kapadia, MD, Section Head of Invasive and Interventional Cardiology at Cleveland Clinic. He adds, however, that the evidence is still too preliminary to change practice recommendations: “These are encouraging findings from a large contemporary cohort of TAVR patients, but they are retrospective and must be viewed as hypothesis-generating until confirmed in a large randomized trial.”
Such a trial might also help clarify one of the study’s unanticipated findings — namely, that the outcomes benefit observed with RAS inhibitors was most pronounced among patients with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF). “This result surprised us,” Dr. Kapadia says. “In the setting of heart failure, the benefits of RAS inhibitors have been greatest among patients with reduced LVEF. This suggests a possible difference in mechanism of RAS inhibition between heart failure and aortic stenosis.”
The study helps address a dearth of data on the role of RAS inhibitors — i.e., ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) — in patients with aortic stenosis undergoing TAVR. A potential role has been proposed in view of these agents’ modulation of adverse left ventricular remodeling and regression of myocardial hypertrophy.
Some of the first clinical data to support such a role came from a large retrospective Cleveland Clinic study (Ann Intern Med. 2014;161:699-710) showing that RAS inhibitor therapy was associated with increased survival in patients undergoing surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) for severe aortic stenosis. “Our earlier findings in SAVR patients, which showed benefit even in patients with normal ejection fraction, prompted this new analysis in TAVR patients,” explains Dr. Kapadia.
Advertisement
He and colleagues from several other institutions analyzed data from consecutive Medicare enrollees who underwent TAVR between July 2014 and January 2016. The data were drawn from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS)/American College of Cardiology Transcatheter Valve Therapies (TVT) Registry.
Among 21,312 TAVR patients at 417 U.S. sites who met inclusion criteria, 8,468 patients (39.7 percent) were prescribed a RAS inhibitor at discharge. Patients prescribed a RAS inhibitor were more likely to have atherosclerotic comorbidities, lower LVEF, a concomitant beta-blocker prescription and a lower STS Predicted Risk of Mortality score.
To assess the effect of RAS inhibitor therapy on outcomes, the investigators matched these patients with similar TAVR patients from the registry who had no RAS inhibitor prescription at discharge, using propensity scoring to account for potential confounding variables. The result was a final study cohort of 15,896 patients — 7,948 with a RAS inhibitor prescription and 7,948 without a prescription. Mean age was 82.4 years, and 48 percent of patients were women.
The primary end points were mortality and hospitalization for heart failure in the year after TAVR. Comparison of the groups with and without a RAS inhibitor prescription revealed the following:
Advertisement
When mortality outcomes were stratified by patients’ LVEF, RAS inhibitor therapy was associated with significantly reduced mortality among patients with preserved LVEF (> 40 percent) (HR = 0.78; 95% CI, 0.71 to 0.86) but not among those with reduced LVEF (≤ 40 percent) (HR = 0.95; 95% CI, 0.81 to 1.12).
“The latter finding contrasts with current guidelines recommending RAS inhibitor therapy only for patients with reduced LVEF in the context of heart failure,” observes Dr. Kapadia. “This warrants further investigation.”
“This is the first study we know of to demonstrate that prescribing a RAS inhibitor at discharge after TAVR is associated with significant reductions in both mortality and heart failure admissions,” Dr. Kapadia points out. He says the next step is a prospective randomized trial to confirm these findings, adding that some additional insights may come from the ongoing RASTAVI trial of ramipril after TAVR.
He notes that the potential utility of RAS inhibitor therapy after TAVR will only expand if TAVR gains regulatory approval for use in patients with aortic stenosis at low surgical risk. “If RAS inhibition is found to promote survival in TAVR patients, it could hold particular appeal in younger patients at low surgical risk,” he says.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
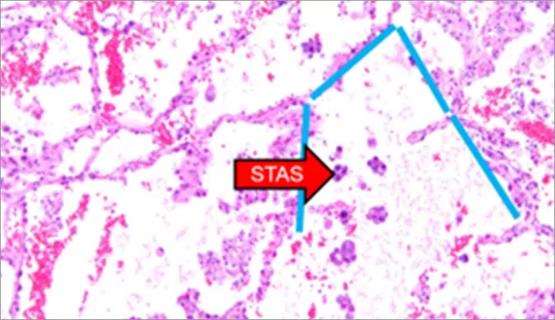
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable