Public reporting is evolving fast. Are you keeping up?

National-level public reporting of clinical outcomes in cardiovascular care began in 2011 with voluntary reporting of metrics from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons’ (STS) Adult Cardiac Surgery Database. As healthcare shifts toward ever-greater transparency, new public reporting initiatives are proliferating. The editors of Consult QD thought the time was ripe for a primer on this fast-evolving area.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A: Less than you may think. Only audited clinical registry data contain the granularity needed to provide the meaningful information that payers, policymakers and patients increasingly demand. Such data typically include metrics for outcomes, structure and process, and they allow for risk adjustment to enable fair evaluation according to severity of patient mix.
In contrast, outcomes reports based on administrative data lack the critical clinical information about patients to provide truly credible, relevant information. As a result, these types of reports are not considered publicly reported data by key stakeholders.
Although several U.S. states have long mandated reporting of selected cardiac surgery outcomes, the only clinical registry data on cardiovascular practice that have been publicly reported at the national level in recent years are from two STS databases: the Adult Cardiac Surgery Database and the Congenital Heart Surgery Database. But new initiatives for national-level public reporting of more clinical registry data are in the works (see final question).
A: Whoever chooses to. Public reporting from the STS registries (and soon-to-come reporting from American College of Cardiology [ACC] registries — see below) is voluntary. While the STS reports that over 90 percent of U.S. adult cardiac surgery centers participate in STS registries, not all of them voluntarily report their data.
For instance, Cleveland Clinic is the only one of the top 10 U.S. heart programs (according to U.S. News & World Report, 2014-15) with publicly reported data in all three categories of the STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database for the July 2013-June 2014 reporting period. (The categories are coronary artery bypass graft surgery [CABG], aortic valve replacement [AVR], and combined CABG + AVR procedures.) The other nine programs either did not publicly report or did not have sufficient CABG + AVR volume to earn a rating in that category.
Advertisement
A: The central rationale for public reporting is to provide transparency and accountability in outcomes to inform decision-making by patients, payers and policymakers. With greater demand for transparency, public reporting of outcomes should help build public trust and may encourage adoption of best practices by more healthcare organizations.
While the public benefits from these effects of public reporting, it shouldn’t lose sight of the risk of unintended consequences, including potential inducements toward risk aversion in patient selection (i.e., cherry-picking).
A: Various developments are underway or on the horizon:
“Public reporting is here to stay,” says Joseph Sabik, MD, Cleveland Clinic’s Chairman of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery. “Cleveland Clinic is proud to be in the forefront of this movement.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
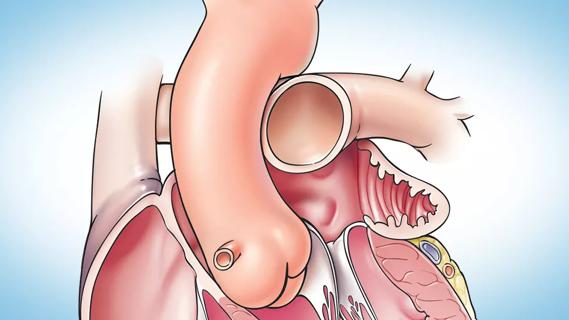
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
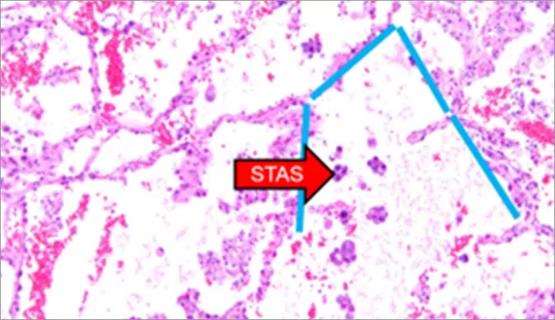
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
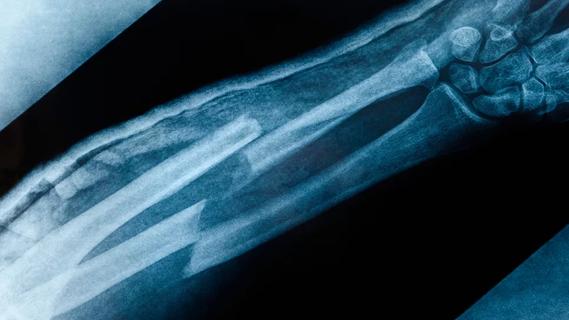
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
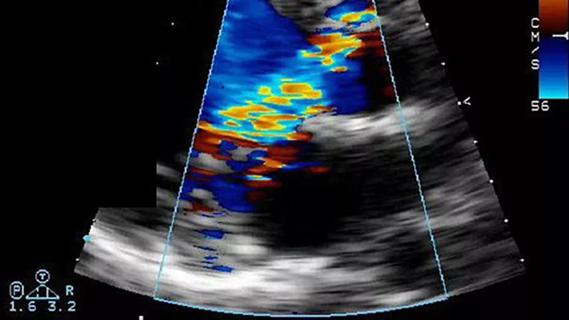
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable