How results changed our practice
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The Protocol T study, conducted by the Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network and sponsored by the NIH, has led to lasting changes in how we manage diabetic macular edema (DME) at Cole Eye Institute.
In this study, 660 adults with visual acuity impairment from DME were randomly assigned to receive intravitreal injections of 2 mg of Eylea® (aflibercept, Regeneron), 1.25 mg of Avastin® (bevacizumab, Genentech) or 0.3 mg of Lucentis® (ranibizumab, Genentech) at 89 clinical sites across the country.
Overall, patients in this one-year study with a two-year follow-up had a significantly better outcome with aflibercept than with the other two drugs. This difference was especially noticeable in patients who had vision worse than 20/50 or retinal thickness more than 400 µm at baseline.
In the past, our practice would have started patients with vision worse than 20/50 on bevacizumab, but now we start them on aflibercept. In patients with vision of 20/40 or better, the study found minimal difference between the drugs, so we start them on bevacizumab since it is much more cost-effective.
Interestingly, in the two-year extension part of the study, the difference between the drugs was no longer statistically significant, in part because many of the patients in the aflibercept group were completely dry on OCT in the first year of study, and that segment continued to have more patients who were dry. Over time, patients in the other groups caught up. If we continued this study for several more years, I suspect all three of the curves would have overlapped because all three agents worked very well.
Advertisement
Safety takes on particular significance when treating a diabetic population. Fortunately, Protocol T found the drugs had a similar safety profile, which is consistent with other comparison studies. An increase in cardiovascular events was found with ranibizumab, but this may have been a statistical anomaly because it hasn’t been seen in any of the other DME clinical trials.
Diabetes is the leading cause of new blindness in the United States, and these anti-VEGF agents offer a safe, effective treatment option for this growing population of patients.
Dr. Kaiser is staff in Cole Eye Institute.
Advertisement
Advertisement
Early data shows risk is 73% higher in patients with lupus, 40% higher in patients with rheumatoid arthritis

Identifies weak spots in the cornea before shape change occurs
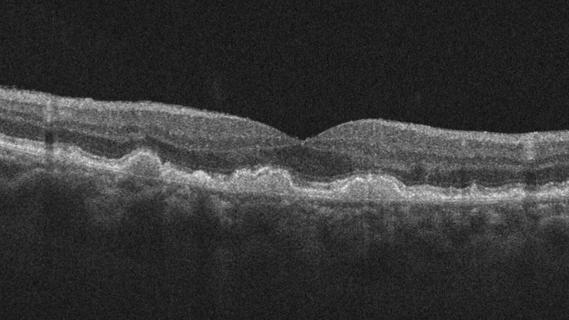
Study highlights the value of quantitative ultra-widefield angiography
Switching medications may decrease treatment burden and macular fluid

Interventions abound for active and stable phases of TED

Corneal imaging and interpretation play a major role
Cole Eye Institute imaging specialists are equal parts technician, artist and diagnostician
Effect of low-dose atropine and dual-focus contact lenses is unknown in patients with comorbid eye conditions