How Cleveland Clinic got a handle on a universal challenge

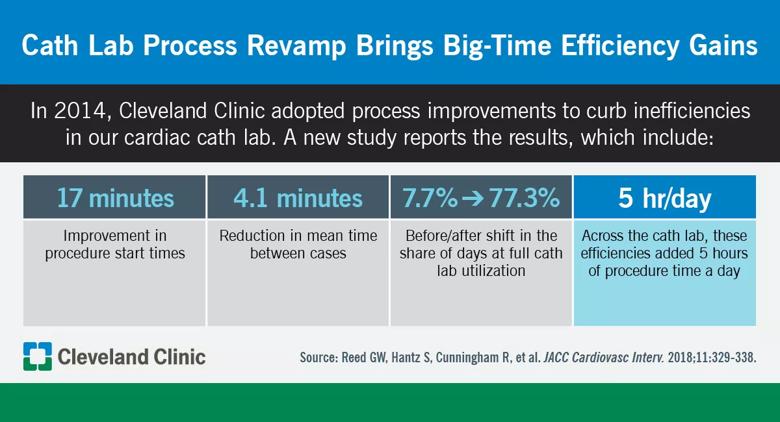
Five additional hours of procedure time each day. That’s what Cleveland Clinic’s catheterization lab achieved through improved start times and reduced turnaround times resulting from a collection of systematic process improvement initiatives designed to reduce inefficiencies. So report a group of Cleveland Clinic clinicians in a new paper in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions (2018;11:329-338).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“This is one of the first and most comprehensive public reports of a quality improvement initiative in a large cath lab,” says the study’s corresponding author, Samir Kapadia, MD, Section Head of Interventional Cardiology and Director of Cleveland Clinic’s Sones Cardiac Catheterization Lab. “Our experience may serve as an example to other institutions that process improvement initiatives like ours can lead to significant cath lab efficiency gains.”
The study examined the effects of new policies implemented in the cath lab in June 2014. The policies resulted from an analysis of cath lab workflow that included creating a process flowchart that outlined and time-stamped every step in a typical patient’s care. Cath lab leadership performed a comprehensive review of the process and identified systematic inefficiencies at several specific steps — along with changes to address them.
Among the most important changes were the following:
Additional changes (among others) included limiting sheath pulls in the cath lab, establishing a central supply system to reduce time spent searching for equipment and downgrading future scheduling priority for attending physicians whose cases were not begun within 15 to 30 minutes of their being paged.
Advertisement
The changes were implemented in a stepwise manner across the cath lab at Cleveland Clinic’s main campus, which includes eight rooms and accommodates a single physician practice of about 20 employed cardiologists.
The study evaluated all elective and urgent procedures performed from one year before to two years after implementation of the new policies. Diagnostic coronary angiograms, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) procedures, right heart catheterizations, myocardial biopsies, peripheral vascular interventions and structural heart interventions were included. Because emergent cases (e.g., primary PCI for ST elevation MI) follow a separate workflow, they were excluded from the analysis.
Comparison of metrics before and after implementation of the process changes revealed significant improvements across a range of measures. Among the key findings:
Notably, these improvements were achieved even as the number of cath lab employees declined from 2013 to 2016 despite steady case volume over the study period. Additionally, there was no increase in weekend, after-hours or overtime shifts, and improvements were observed in all measured aspects of cath lab employee experience, including employee satisfaction.
Advertisement
“Overall, our changes led to a gain of 5.1 to 5.6 hours per day in lab utilization resulting from improved start times and reduced turnaround times,” says cath lab manager and study co-author Scott Hantz, MSN, MBA.
In an editorial accompanying the study in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, two cardiologists from UF Health at the University of Florida, Gainesville, write that the Cleveland Clinic authors “are to be congratulated for tackling some of the issues of inefficiency most catheterization laboratories deal with and approaching the task with scientific rigor.”
The editorialists single out “the assembly of stakeholders across the spectrum of care for patients who interact with the catheterization laboratory” as a key achievement of this work. “The importance of this type of teamwork should not be underestimated,” they write, noting that this may be the aspect of the project that is most easily translatable to other institutions.
Indeed, translation of this approach is something that Cleveland Clinic’s Dr. Kapadia and his co-authors are hoping their study will engender. “We’re moving toward a reality where more and more cardiovascular care will be reimbursed through models like bundled payments that emphasize quality over quantity,” he says. “That makes utilizing resources as effectively and efficiently as possible — as we’ve aimed to do with our cath lab process improvements — a paramount consideration for all institutions.”
As for next steps, Dr. Kapadia says “we plan to continue this initiative and find ways to expand it to other services provided in the cath lab,” such as electrophysiology, aortic endovascular and interventional radiology procedures.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable