1,000-patient prospective trial to start enrolling patients soon
When the PROACT Xa multicenter randomized trial starts enrolling patients later this year, it will be aiming to answer a long-standing question: Can patients consider surgical aortic valve replacement (AVR) with a mechanical valve without the need for the monitoring requirements of warfarin?
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“Currently, warfarin is the only approved anticoagulant for patients receiving mechanical valves,” says Cleveland Clinic Heart, Vascular & Thoracic Institute Chair Lars Svensson, MD, PhD, who’s serving as co-chair of the PROACT Xa steering committee. “The results of this prospective study could ultimately allow younger AVR candidates to choose a valve that has excellent long-term durability along with a much simpler way of managing their anticoagulation by just taking daily pills without the INR monitoring required with warfarin.”
The daily pills would be the oral factor Xa inhibitor apixaban, which is approved for stroke prophylaxis in atrial fibrillation and treatment of venous thromboembolism but not for anticoagulation following AVR.
PROACT Xa investigators will enroll 1,000 patients who have undergone AVR with the On-X mechanical aortic valve at least three months previously and been started on anticoagulation with warfarin. Patients will be randomized from over two dozen U.S. centers, including Cleveland Clinic, to either continue warfarin or be switched to apixaban 5 mg or 2.5 mg twice daily.
Patients will be followed for two years to determine whether apixaban:
Dr. Svensson notes that the PROACT Xa study is being launched in the context of declining use of mechanical valves for AVR. “An obvious reason is because patients don’t want to have to take warfarin,” he says. “Additionally, younger patients believe that if they have AVR with a biologic valve, they will always have the option of having TAVR [transcatheter AVR] down the road” if the biologic valve starts to degrade.
Advertisement
But he cautions that this calculation must not underestimate how long patients might live with their second replacement valve. “We don’t yet know the long-term durability of TAVR valves,” he says. “Additionally, there is some evidence of increasing risk of stroke and mortality over time in TAVR patients,” he adds, pointing to the recent publication of five-year outcomes from the PARTNER 2 trial showing crossing trend lines for risk of stroke and death with TAVR and surgical AVR in intermediate-risk patients (N Engl J Med. 2020;382:799-809).
He also observes that there are data showing superior patient survival and valve function with mechanical versus biologic aortic valves, both in studies of AVR generally and in a large review of Cleveland Clinic experience with aortic root procedures in over 950 patients (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2016;151:764-774).
“The pendulum may have swung too far away from mechanical valves in younger patients,” Dr. Svensson says, noting that this is one reason the PROACT Xa trial (NCT04142658) is being undertaken.
If the study meets its specified endpoints, Dr. Svensson believes it would make AVR with a mechanical valve more attractive to younger patients, although he says it’s not clear if such findings would hold for mechanical valves other than the On-X prosthesis or for direct oral anticoagulants other than apixaban. “Those questions would require separate randomized controlled trials,” he says.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
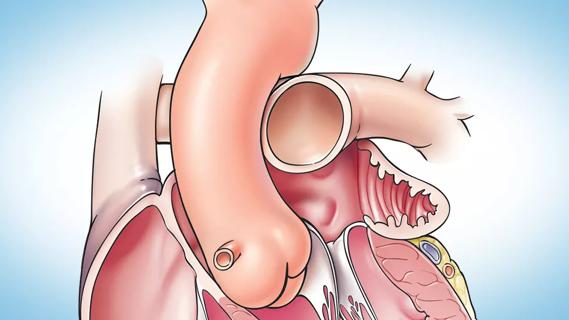
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
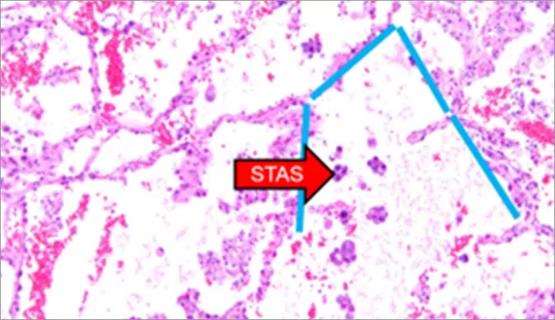
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
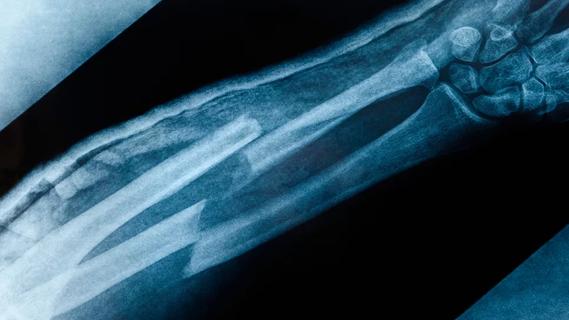
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
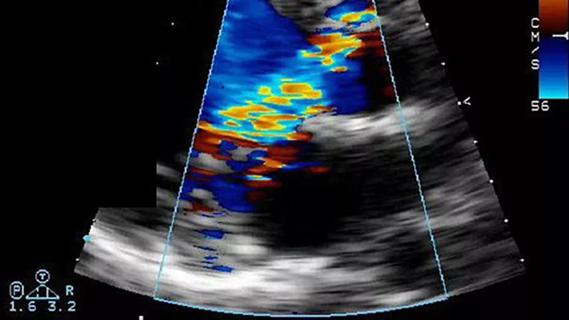
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
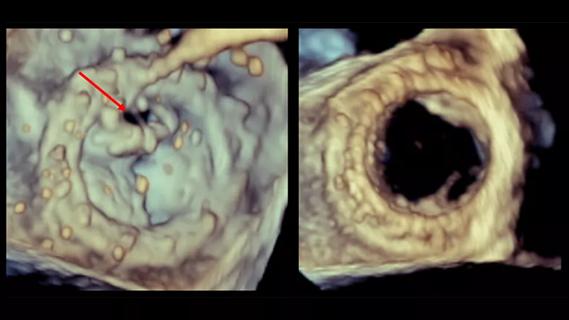
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable