Dr. Steven Nissen shares his take
Now that publication of the FOURIER trial of evolocumab has yielded the first large-scale clinical outcomes data for a PCSK9 inhibitor, the question naturally arises: “Who should be treated?”
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
In this two-minute video, Cleveland Clinic Cardiovascular Medicine Chairman Steven Nissen, MD, shares his thoughts on that question and also sums up current understanding of the safety of intensive LDL cholesterol lowering with PCSK9 inhibitor therapy.
For a related video recap of all major PCSK9 inhibitor study presentations at the American College of Cardiology meeting (ACC.17), click here.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
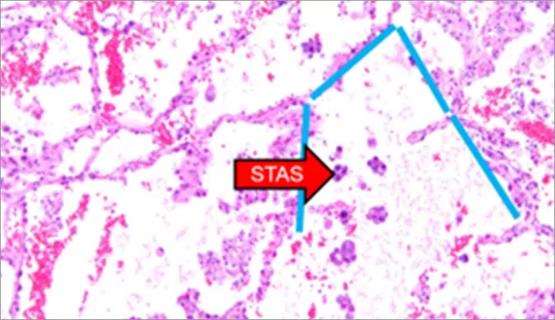
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable