Unprecedented LDL-C reductions raise hopes for long-term outcome trials
The investigational lipid-lowering agents known as PCSK9 inhibitors have come a long way in a short time — especially in terms of their potential for use in combination with statins for:
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“This drug class is moving rapidly from bench to bedside,” says Steven Nissen, MD, Chairman of Cleveland Clinic’s Department of Cardiovascular Medicine. “The target (see “Fast Facts” sidebar) was identified just a few years ago, and now large outcomes trials are underway.”

2014 was a pivotal year for presentations of PCSK9 inhibitor studies (including those reviewed here) demonstrating promising results in a broad spectrum of patients with hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia, according to Michael Rocco, MD, Medical Director of Cardiac Rehabilitation and Stress Testing in Cleveland Clinic’s Section of Preventive Cardiology. “In these studies, many of which spanned a year or more, consistent lowering of LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) was achieved, with sustained benefits over time, excellent tolerability and very few serious side effects,” he says.
Several PCSK9 inhibitors are in the development pipeline. “Even with different products, the studies have been very consistent in the degree of LDL-C lowering across a broad range of patients,” Dr. Rocco notes. These include patients who are high-risk, those with familial hypercholesterolemia and those who are statin-resistant. The reductions have ranged from about 48 percent to 70+ percent, depending on the study, with LDL-C levels reaching the range of 20 to 50 mg/dL in some cases.
“Unprecedented” is how Dr. Nissen characterizes PCSK9 inhibitors’ ability to lower LDL-C, adding: “We have not seen any evidence in emerging trials that the LDL-C levels achieved are producing any harm. Even the very, very low levels appear to be safe.”
Advertisement
He notes, however, that it will take a few years of outcomes trials to demonstrate whether these very low LDL-C levels yield important reductions in morbidity and mortality.
Dr. Nissen says researchers are “cautiously optimistic” that one or more PCSK9 inhibitors will be approved by the FDA as add-on therapy in 2015, for indications related to the specific high-need patient groups mentioned above. The two agents that currently appear closest to potential approval are Amgen’s evolocumab and Sanofi and Regeneron’s alirocumab.
Positive results were reported last year for both evolocumab and alirocumab at major cardiology meetings. While favorable clinical results also have been reported for Pfizer’s bococizumab, it falls in the middle of development pack, followed byLilly’s LY3015014, which may offer a different dosing regimen, and PCSK9 inhibitors from Roche and Alnylam.
2015 should bring additional safety and durability results from ongoing open-label trials with longer follow-up than previous studies. More patient subgroup study results are also likely this year.
Dr. Rocco says there is a growing need for new options like PCSK9 inhibitors in difficult-to-treat and statin-intolerant patients: “One in 250 to 500 people have familial hypercholesterolemia. Large numbers of patients are at least partially intolerant of statins. And myalgia is reported in substantial numbers of patients on statin therapy — 2 to 3 percent in clinical trials and as many as 10 to 20 percent in observational studies. This represents a large population for which there are limited treatment options.”
Advertisement
Dr. Nissen notes that studies are showing that even patients previously intolerant of statins may be able to tolerate them at lower or less-frequent doses when used with a PCSK9 inhibitor — while still realizing the benefits of significantly lower LDL levels. He adds that patients who previously could not reach LDL-C targets on maximal statin therapy also are seeing significant reductions with PCSK9 inhibitor add-on therapy.
FDA approval of PCSK9 inhibitors for these targeted indications would likely be a gateway to broader use, according to Dr. Rocco. He expects that additional indications would follow pending results of large outcomes trials gauging whether PCSK9 inhibitors’ LDL-C reductions translate to fewer major cardiac events, including cardiac-related deaths.
The three major outcomes studies underway for evolocumab, alirocumab and bococizumab collectively include 50,000 to 60,000 higher-risk patients, so the results will be reflective of large patient populations.
Meanwhile, a post hoc analysis presented at the American Heart Association’s 2014 scientific sessions suggested that PCSK9 inhibitors’ LDL-C-lowering abilities may ultimately be shown to reduce major cardiac events, Dr. Rocco says. The analysis pooled results of five alirocumab trials, which included 3,500 patients followed for at least a year, to retrospectively assess cardiac endpoints, including cardiac death. The 65 percent hazard ratio represented a robust reduction, although the finding did not quite reach statistical significance, due in part to the low number of events.
Advertisement
“While larger prospective controlled outcomes trials are needed, this post hoc analysis supports the notion that this degree of LDL-C reduction may be associated with long-term outcomes benefits,” Dr. Rocco says. “It suggests we’re headed in the right direction.”
Demonstrating positive outcomes with optimal LDL-C control also will be important for convincing payers to cover PCSK9 inhibitors, since these monoclonal antibodies are expected to be much more costly than statins and other dyslipidemia therapies.
While the FDA is currently considering PCSK9 inhibitors only as combination therapy with statins, not as monotherapy, Dr. Nissen notes they may ultimately have a role as monotherapy in certain settings. “It’s an evolution,” he says. “It will take time to figure it all out.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
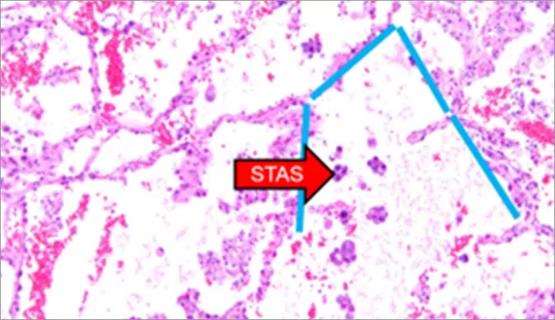
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
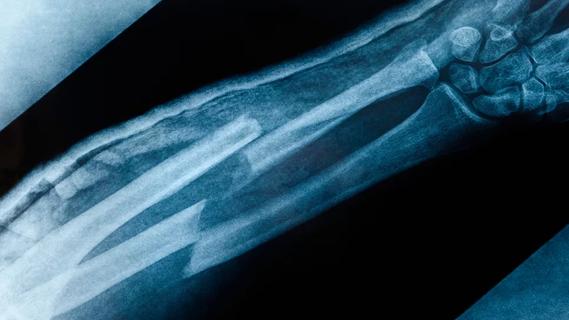
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable