New, valid tool for falls assessment
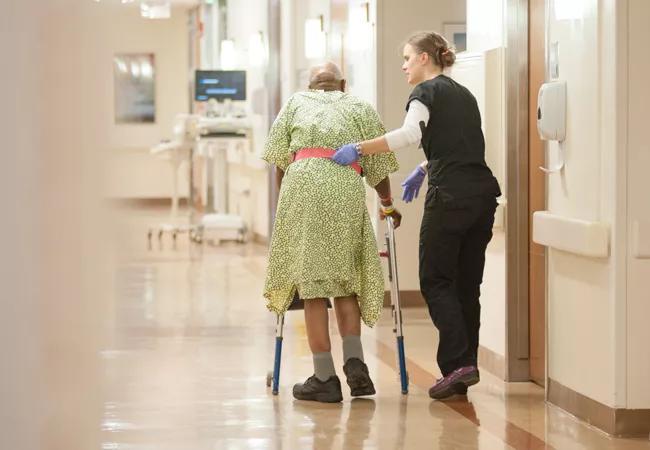

Nursing research is often like stepping stones, with one project building upon an earlier one. That’s the case for a study conducted by Samantha Weed-Pfaff, BSN, RN, in 2012. As a nurse in Cleveland Clinic’s palliative medicine unit, Weed-Pfaff agreed to lead a research study to validate a risk score tool that provided predictors of fall events in hospitalized patients with cancer. The predictors had been derived by Luann Capone, MSN, MPA, RN, GNP-BC, and Nancy Albert, PhD, CCNS, CHFN, CCRN, NE-BC, FAHA, FCCM, FAAN, in previous research. Capone is a nurse practitioner in Cleveland Clinic’s Connected Care program, and Dr. Albert is the healthcare organization’s Associate Chief Nursing Officer for Research and Innovation.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Research has always sparked Weed-Pfaff’s interest, and as a new graduate nurse working on the palliative medicine unit she had questions about nursing practice on the floor. Weed-Pfaff presented an idea for a small unit-based research project at a meeting, where she also heard Dr. Albert talk about the Cleveland Clinic Capone Albert (CC-CA) Falls Risk Assessment tool.
“When she described the huge difference between the rate that medical/surgical patients and oncology patients were falling, I was shocked,” says Weed-Pfaff, now an assistant nurse manager in the palliative medicine unit. “Nancy suggested a validation study of the tool, and I got on board!” Weed-Pfaff began by learning as much as possible about Capone and Albert’s research.
During the first phase of Capone and Albert’s research, published in the Journal of Nursing Care Quality (July/September 2010), authors described characteristics of 158 hospitalized cancer patients who fell and in the paper, shared similarities and differences from published reports of adult medical/surgical hospitalized patients who fell.
In the second phase, Capone and Dr. Albert derived predictors of fall events in hospitalized patients with cancer and then developed a risk score tool based on the predictors. Results were published in the Oncology Nursing Forum (September 2012) and included a nomogram to assess fall risk using the identified predictors: abnormal gait, cancer type, presence of metastasis, antidepressant and antipsychotic medication use during the hospital stay and blood product infusion during the hospital stay.
Advertisement
The goal of the prospective study Weed-Pfaff led was to validate the accuracy of the six factors of the CC-CA Falls Risk Assessment tool in a new group of patients with cancer. Validation of the factors would ensure the tool’s readiness for clinical use and generalizability to all patients with cancer. In this phase of research, Pfaff and Dr. Albert also compared the CC-CA tool to the Morse Falls Scale traditionally used to assess falls risk.
Weed-Pfaff and co-investigators reviewed medical records of nearly 1,800 patients admitted and treated for cancer in acute care units at four Cleveland Clinic hospitals and the palliative medicine unit on main campus. “Before initiating data collection, we discussed that the CC-CA Falls Risk Assessment tool would be clinically important if the concordance index exceeded the Morse Falls Scale in discrimination by at least 10 percent,” says Weed-Pfaff. The concordance index provides the probability that the predicted fall risk score discriminates low and high events to closely match observed (actual) fall events.
In analysis, the CC-CA Falls Risk Assessment tool was superior to the Morse Falls Scale. “The Morse tool had a concordance index of 0.60 in predicting falls, and the CC-CA tool had a concordance index of 0.80,” says Weed-Pfaff. The research project methods and findings were accepted for publication in the Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing, with a print date scheduled for October 2016.
Weed-Pfaff believes the results can influence nursing practice. “Knowing which risk factors are the most important predictors of fall events among adults with cancer is very helpful,” she says. “We can implement general falls prevention strategies with all patients, and then, based on the CC-CA Falls Risk Assessment tool results, escalate and individualize strategies to prevent falls and fall-related injuries.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
Nurses play key role in comprehensive lifetime treatment program

Customized bots improve speed, efficiency by streamlining daily clinical, clerical tasks

Nurses play pivotal role in patients’ ability to recover in the comfort of their own homes
New protocol reduces costs, increases patient and caregiver satisfaction

Advocating for patient safety is imperative in fast-paced surgical settings

M-Power program improves the perinatal experience for people who have survived abuse

Advice for those pursuing a WOC nursing career

Veteran nurse shares his experience as a caregiver and community volunteer