The case for incorporating behavioral health services into cardiology clinics
Among the many factors to be considered in properly diagnosing and treating cardiovascular disease, the patient’s mental health may be the most overlooked. Cardiac events can be major sources of stress and anxiety, even after they have been identified and have abated.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“It’s an unexpected encounter for many patients,” says Leo Pozuelo, MD, Section Head of Cleveland Clinic’s Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry Service. “Quite often, heart disease will throw patients for a loop because it’s a brush with their mortality. There is also a subset of patients who have pre-existing depression or an emotional issue that is exacerbated by the ordeal.”
Dr. Pozuelo leads Cleveland Clinic’s Cardiovascular Behavioral Health Clinic, which addresses these concerns. The clinic is housed within the Section of Preventive Cardiology and Cardiac Rehabilitation as a consultation service available to the patient, the treating cardiologist and the patient’s primary care physician.
“Cardiovascular medicine has progressed substantially to the point that the emotional coping and wellness of a patient is taken into consideration along with physical coping and wellness,” he says. “To facilitate and coordinate care, it is now well recognized that co-location of behavioral health services within cardiology clinics is most beneficial.”
As part of the standard intake process, patients in preventive cardiology and those enrolled in the cardiac rehabilitation program are evaluated to determine how well they are coping emotionally in the wake of cardiovascular surgery or other potentially traumatic therapies. Quality-of-life scores coupled with screening questions on depression and anxiety help determine which patients could benefit from the Cardiovascular Behavioral Health Clinic.
Advertisement
“These patients often won’t take their medications, won’t see their physician, won’t stop smoking and won’t take any of the other steps necessary for their recovery,” says Leslie Cho, MD, Section Head for Preventive Cardiology and Cardiac Rehabilitation and Director of the Women’s Cardiovascular Center. “It’s no longer enough for a cardiologist to simply tell them, ‘You’re fine.’ There’s a great need for psychiatric intervention, given the common occurrence of depression after these life-changing events.”
Dr. Pozuelo identifies three major benefits of the Cardiovascular Behavioral Health Clinic:
That last point is key, says Dr. Cho. “Many elderly patients don’t want to go to the psychiatry building,” she says. “There’s a stigma attached to it, so they stay with us in the cardiology clinic, which is where Dr. Pozuelo sees them. The stigma is completely gone.”
While each case is unique, some general approaches to behavioral health care are efficacious for many patients. “When we see a patient in this type of clinical encounter, we try to point out their strengths and resiliency and help them identify steps that have helped them through difficult times before,” says Dr. Pozuelo.
Advertisement
“Taking the time to have that conversation is vital and helps patients understand that they’re equipped to deal with the stress of heart disease,” he adds. “A behavioral health cardiology clinic can facilitate patients’ recovery and hopefully improve their quality of life.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
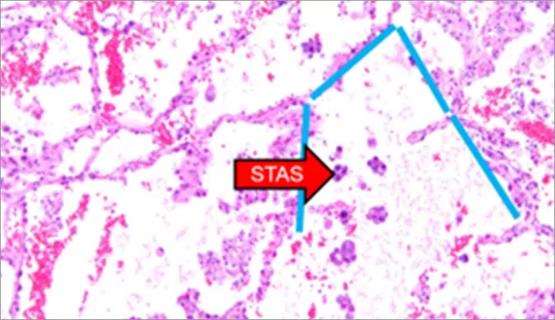
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
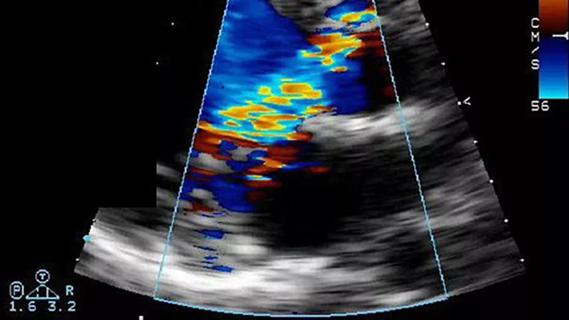
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
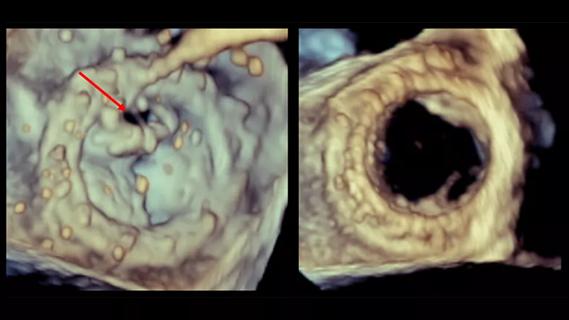
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable