Case shows planning and careful monitoring can overcome high risks
By David Majdalany, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 32-year-old woman with Shone’s complex, Graves’ disease (treated with radioactive iodine in 2004) and obesity (BMI 45 kg/m2) presented to Cleveland Clinic’s Cardio-Obstetrics Clinic at 7 weeks’ gestation. She was born with coarctation of the aorta, a parachute mitral valve and a bicuspid aortic valve. At age 3 years, she had repair of her coarctation of the aorta, which consisted of resection and end-to-end anastomosis. Three months before presentation, she underwent aortic valve balloon valvuloplasty for aortic stenosis. She had an acute mid-to-upper cerebellar cardiovascular accident, presumably from endocarditis, and was treated with antibiotics. No arrhythmias were noted on month-long rhythm monitoring, and testing for hypercoagulable state was unremarkable.
At presentation, she reported no symptoms and no limitations in ordinary activity (NYHA class I).
Shone’s complex, a developmental sequence of abnormalities on the left side of the heart and aorta, has a prevalence of less than 1 percent among adults with congenital heart disease. Its cardinal features are:
Partial presentations with just two or three features may occur. Although morbidity in adulthood is low, pregnancy carries a WHO class 3 or 4 rating (relatively or absolutely contraindicated, depending on severity) due to significant risk of severe morbidity or death.
Evaluation of the patient by transthoracic echocardiography revealed moderate-to-severe aortic stenosis and mild aortic regurgitation (peak/mean gradients = 66/35 mmHg) (see Figure 1).
Advertisement
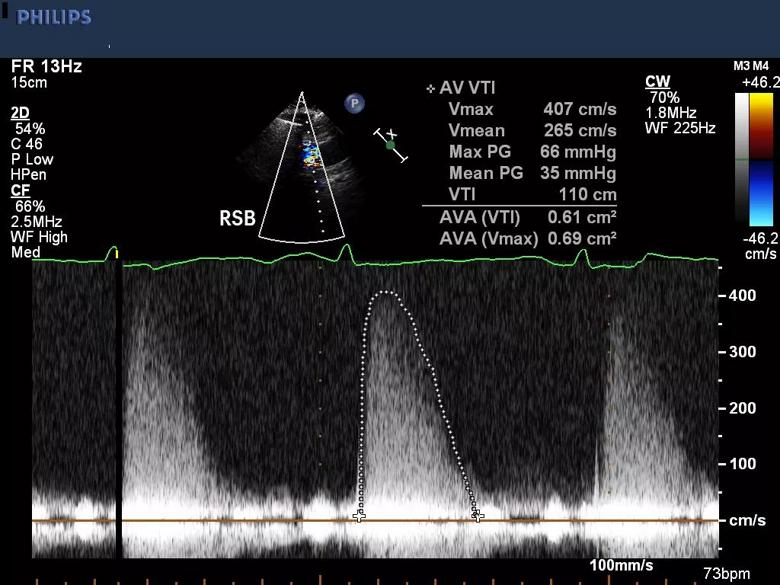
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/7d2b3f3e-2a2c-4801-8287-81532d111f9a/18-HRT-4764_Shones-case_Inset-1_jpg)
Figure 1. Transthoracic echocardiogram at presentation showing moderate-to-severe aortic stenosis by gradients.
Biventricular size and function were preserved, left ventricular hypertrophy was present, and moderately elevated gradients were observed across the parachute mitral valve (peak/mean gradients = 20/8 mmHg [heart rate, 73 bpm]) (Figure 2).
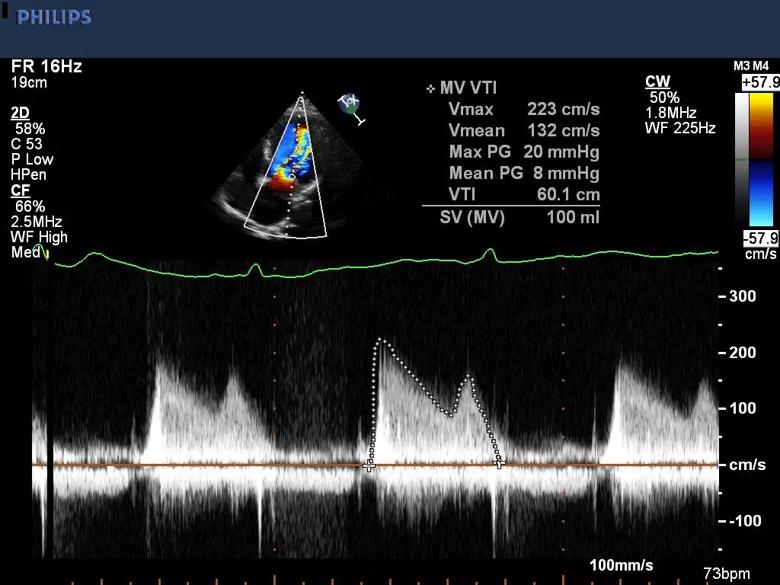
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/8f2c8fc1-746a-4d83-8615-61bf37e73043/18-HRT-4764_Shones-case_Inset-2_jpg)
Figure 2. Transthoracic echocardiogram at presentation showing moderately elevated gradients across the patient’s parachute mitral valve.
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of the aorta (Figure 3) revealed no focal narrowing, aortopathy or enlargement of the mid-ascending aorta.
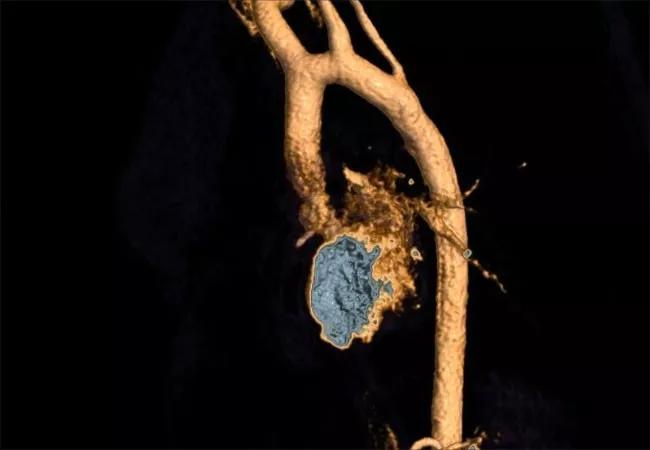
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/56e8b435-f102-465a-bee9-a498c376bdac/18-HRT-4764_Shones-complex-650x450_jpg)
Figure 3. Magnetic resonance angiogram of the patient’s aorta at presentation showing no focal narrowing, aortopathy or mid-ascending aorta enlargement.
In 2011, the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) published guidelines on managing cardiovascular diseases during pregnancy. The CARPREG risk score, based on the following four predictors, is widely used to estimate risk of a cardiovascular complication and has been validated in several studies:
With a point assigned for each predictor present, risk is estimated as follows:
Advertisement
Our patient had at least two points because of her TIA and severe aortic stenosis — as well as mitral stenosis, albeit moderate — putting her at high risk for a cardiovascular complication.
She was counseled on her risks of heart failure and arrhythmias, as well as the possible need for intervention on her aortic valve during the pregnancy. She was further advised about the risks to the fetus, including prematurity, intrauterine grown retardation, low birth weight, mortality, and risk of congenital heart disease. She elected to continue the pregnancy.
The patient was followed throughout her pregnancy in Cleveland Clinic’s multidisciplinary Cardio-Obstetrics Clinic. She was seen every four weeks (every two weeks during the third trimester) and had monthly echocardiograms.
Her echocardiogram at 15 weeks’ gestation showed a mild increase in aortic stenosis, with a peak gradient of 86 mmHg (vs. 71 mmHg six weeks earlier) and a mean gradient of 49 mmHg (vs. 44 mmHg earlier). This was not unexpected, given increased plasma volume and cardiac output during pregnancy. Repeat testing throughout the rest of pregnancy showed elevated stable aortic and mitral valve gradients.
Fetal echocardiography at 24 weeks revealed normal fetal cardiac anatomy.
She was diagnosed with gestational diabetes at 30 weeks, which was controlled with diet.
She underwent weekly non-stress testing starting at 32 weeks.
Labor was induced at 39 3/7 weeks with oxytocin and misoprostol (to reduce bleeding) with the goal of avoiding hypotension and tachycardia. Latent-phase arrest prompted cesarean section delivery. The healthy baby girl (9 lb, 6 oz) was taken to the well-baby nursery.
Advertisement
The mother was admitted to the ICU after delivery for monitoring. Postpartum hemorrhage was suspected due to vaginal bleeding and a drop in the hemoglobin level on the complete blood count. She received a blood transfusion and was taken to the operating room for dilation and curettage. In total, she received 5 units of packed red blood cells, 1 unit of fresh frozen plasma and 10 units of cryoprecipitate to maintain hemoglobin above 9 g/L.
The mother was monitored in the ICU for 48 hours with no recurrent bleeding and was discharged home on postoperative day 5 with a healthy baby girl. At her six-week obstetric follow-up appointment, the patient was asymptomatic.
Limited literature is available for managing pregnancy in women with Shone’s complex. This case illustrates several key points:
Advertisement
Advertisement
A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery
Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation
Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable