A key link for exceptional care across the life continuum
Your healthcare organization may provide exceptional care, but is it doing so through the very end of your patients’ lives?
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
That’s a question that recently prompted Cleveland Clinic to rethink when and where it was offering hospice services for inpatients dying from advanced cardiac illnesses. As a result, now when patients with terminal conditions have truly exhausted all treatment options — including for cardiovascular conditions such as advanced heart failure or complications from an LVAD — an inpatient hospice service is available to come to the patient in the ICU or hospital room, often avoiding the need for transfer to an external location.
“Cleveland Clinic is not just there for patients when things are going great,” observes heart failure cardiologist Eiran Gorodeski, MD, MPH. “We are proud to also offer highly specialized services to patients at this critical point in their lives.”
Up to 2014, Cleveland Clinic Hospice provided care at home, in nursing homes and at Cleveland Clinic’s regional hospitals, but it did not offer inpatient hospice care at the health system’s flagship main campus hospital. In October of that year, increasing recognition of the need for more expertly nuanced care at the end of life prompted extension of the program’s hospice services to patients throughout the 1,400-bed main campus hospital.
“Because our hospital is large and complex, and because these patients are very sick, we decided to send our hospice team to the ICUs and floors where patients are actively dying,” Dr. Gorodeski explains.
In 2016, this inpatient hospice service was employed for 435 patients at Cleveland Clinic, 47 of whom were patients with end-stage cardiovascular disease.
Advertisement
Most often, an ICU team initiates a hospice consult. A hospice nurse evaluates the patient and speaks with the patient and family. If everyone agrees to proceed, the patient is transitioned from acute care to hospice care in place.
Primary goals are controlling symptoms, such as pain and shortness of breath, and making sure the patient does not suffer. When necessary, compassionate extubation is performed in a controlled setting.
“Our inpatient hospice team delivers care that is complementary to the care from the ICU team, allowing them to better focus on their intensivist expertise,” says Dr. Gorodeski.
The inpatient hospice team includes a hospice and palliative medicine board-certified physician, a nurse, a social worker and a chaplain to ensure that each patient’s individual spiritual, emotional, psychological and physical needs are met.
An important aspect of care is providing guidance about what to expect, according to Laura Hoeksema, MD, MPH, the hospice physician who leads the team. “Death can be scary,” she says. “We work to reduce that fear and help patients and families prepare by educating them about what will happen over the next few hours or days.”
She adds that the team may recommend “closure activities,” which Dr. Hoeksema describes as “conversations patients may want to have with loved ones before losing the opportunity to do so.”
Although a handful of programs like this exist in the U.S., dedicated hospice units are far more common. Cleveland Clinic is now evaluating the value offered by its inpatient hospice team by interviewing families of cardiovascular disease patients who died on the hospice service and comparing their comments with those from families whose loved ones died on the cardiac service.
Advertisement
The inpatient hospice service is currently offered only on Cleveland Clinic’s main campus; at regional hospitals, inpatient hospice care is provided by the admitting physician with support from the interdisciplinary hospice team.
But Dr. Hoeksema is hopeful the model will eventually be employed at regional hospitals as well. “I am proud to work in a health system committed to providing excellent care across the continuum of life,” she says.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
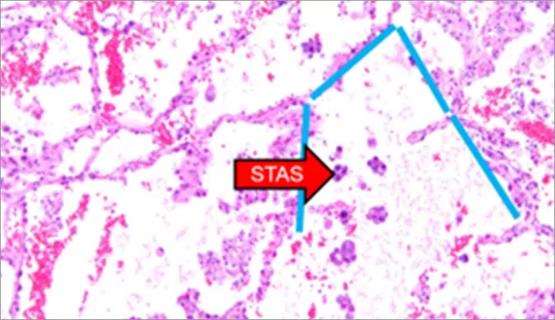
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
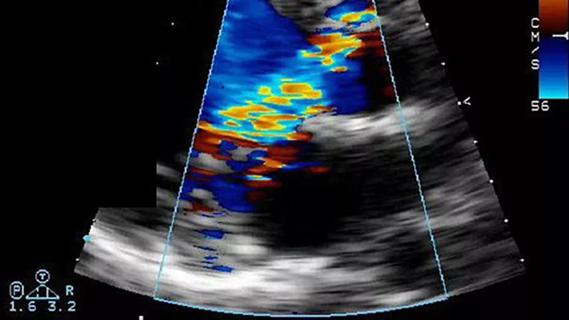
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
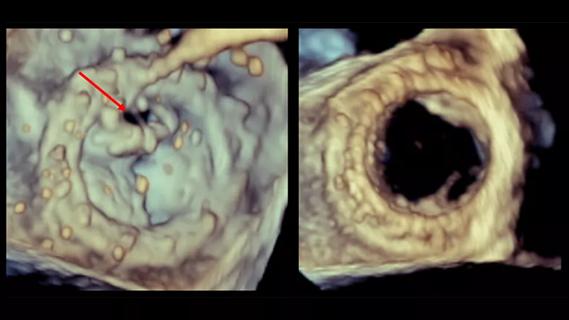
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable