Echo findings in young athletes are not always what they seem

Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A white male high school basketball player undergoes an ECG and echocardiogram after presenting with atypical chest pain. Although the ECG is unremarkable, he is disqualified from competitive sports because of concern for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) after the echo reveals septal wall thickness of 1.5 cm. He has no family history of HCM.
He comes to Cleveland Clinic’s Sports Cardiology Center for a second opinion. The septal wall measurements are confirmed on echocardiogram (left image below). While up to 18 percent of African-American athletes have septal wall thickness greater than 12 mm, this finding is unusual in a white athlete. However, diastolic function and longitudinal strain are normal (see systolic strain profile at bottom of post).
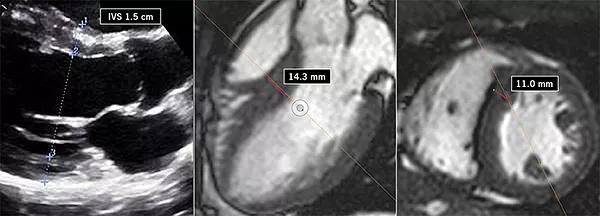
He performs well on a metabolic stress test (VO2 max is 64.3 mL/kg/min), and MRI reveals no scar and a normal mitral valve apparatus. Close evaluation of the MRI reveals that the septal measurement from long-axis view was overestimated due to a tangential cut through the septum and inclusion of right ventricular trabeculation (middle image above). The true septal measurement is determined to be 11 mm (right image above). The collective findings are believed to be related to “athlete’s heart,” and the patient is allowed to return to play.
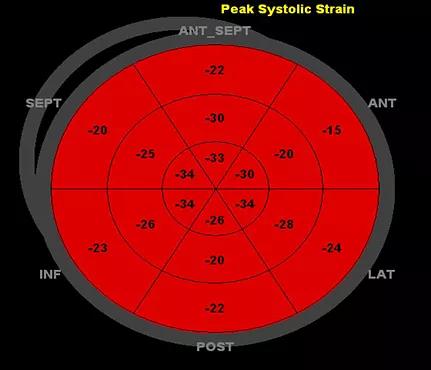
The patient’s systolic strain profile.
For more on athlete’s heart, see this companion Consult QD post .
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable