JACC review highlights factors unique to women, ways to tailor management
Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and gestational diabetes mellitus (DM) put women at elevated risk for cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life, and early primary prevention to address these and other conditions unique to women can improve eventual outcomes. So contends a new Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) State-of-the-Art Review (2020;75[20]:2602-2618) summarizing updated recommendations for the primary prevention of CVD in women.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
The document, developed by the ACC’s Cardiovascular Disease in Women Committee, is an update to a 2011 guideline update on the topic from the American Heart Association (AHA), which covered only conventional CVD risk factors.
“A plethora of evidence pertaining to women’s cardiovascular risk has emerged in the past decade, enabling JACC to issue the first comprehensive guideline detailing women’s unique risk factors with recommendations for primary prevention,” says lead and corresponding author Leslie Cho, MD, Director of the Women’s Cardiovascular Center and Co-Section Head of Preventive Cardiology and Rehabilitation at Cleveland Clinic.
In addition to covering risks specific to women, the new update discusses traditional CVD risk factors, with an emphasis on distinct manifestations and treatment responses in women. Multiple tables and figures concisely summarize key points and management strategies.
The review discusses — and provides treatment recommendations for — the following disorders that are unique to or likelier to occur in women:
Advertisement
“Many of the conditions unique to women arise decades before cardiovascular disease manifests itself,” she adds. “This creates a huge window of opportunity to take proactive measures that can make a real difference in outcomes.”
The updated guideline also examines how the following traditional CVD risk factors affect women in different ways than men:
Advertisement
The new guideline update also covers anticoagulation therapy for atrial fibrillation, aspirin therapy, perimenopausal hormone therapy and psychosocial issues.
“Cardiovascular disease is preventable in 90% of cases,” concludes Dr. Cho. “Tailoring management with a knowledge of important gender differences helps providers optimize patient care.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
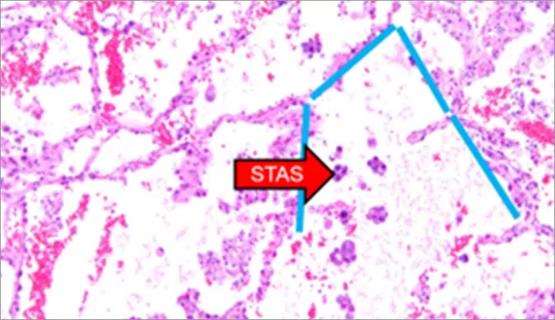
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable