Gracilis transposition is an effective surgical technique for repairing complex perineal fistulas in either gender (rectovaginal fistulas in women and rectourethral fistulas in men).
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
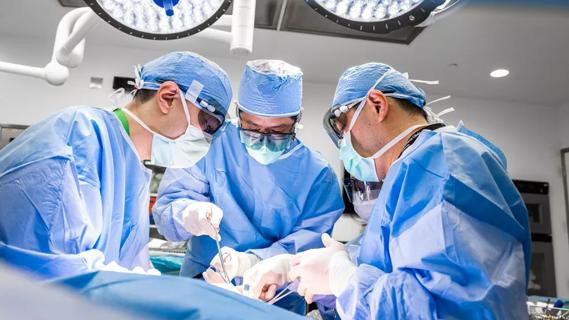
In this video, Steven Wexner, MD, Director of the Digestive Disease Center and Chair of Colorectal Surgery at Cleveland Clinic Florida, explains the procedure step by step in two separate surgical procedures. Watch Dr. Wexner:
The team initially places the patient with the rectovaginal fistula in the modified Lloyd Davies lithotomy position to harvest the gracilis muscle, being careful not to cross the knee joint or injure the vessels triangulated with the nerve, and to ensure that the harvested muscle is indeed gracilis. Before repositioning the patient into the prone jackknife position, the team stabilizes the tendon to a perineal incision.
Once the patient is redraped, the surgeon makes a circumanal incision separating the anterior rectal wall from the posterior vaginal wall coming across the fistula. The team continues to dissect in a cephalad manner into soft, areolar tissue before debriding the fistula. Dr. Wexner notes that surgeons can debride from either the anterior or posterior aspect of the incision. He begins the closure in a cephalad to caudal direction to prevent stricture formation, a common occurrence with large fistulae. Once the closure is complete, he looks at the primary opening to debride it and either close it or leave it open. Postoperatively, the patient remains in bed for three days in an adduction splint and broad-spectrum antibiotics are administered. To watch both this surgery and a rectourethral fistula repair, click above or visit and subscribe to Cleveland Clinic’s YouTube channel.
Advertisement
Advertisement

Strong patient communication can help clinicians choose the best treatment option

ctDNA should be incorporated into care to help stratify risk pre-operatively and for post-operative surveillance

The importance of raising awareness and taking steps to mitigate these occurrences
New research indicates feasibility and helps identify which patients could benefit

Treating a patient after a complicated hernia repair led to surgical complications and chronic pain
Standardized and collaborative care improves liver transplantations
Fewer incisions and more control for surgeons

Caregiver collaboration and patient education remain critical