Expert analysis argues that study design may have disadvantaged CABG
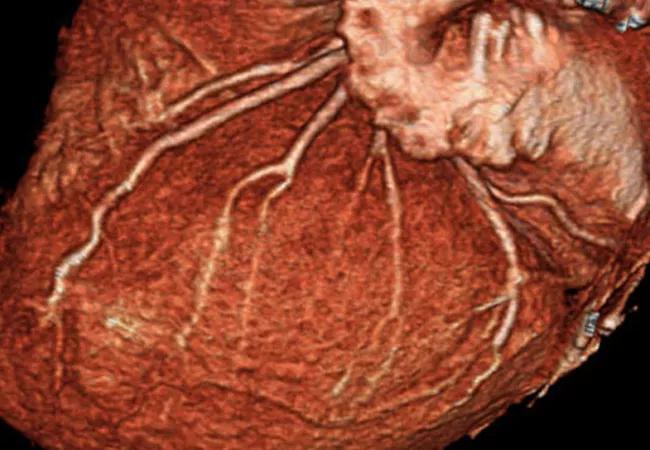
Final results from the largest comparison of revascularization strategies for low-complexity left main coronary disease should not be viewed as the final word on the issue, contend two cardiac surgeons in an invited expert analysis of the EXCEL trial on ACC.org.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Findings at final five-year follow-up from the 1,905-patient randomized trial were recently published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:1820-1830), showing equivalence on the primary outcome — a composite of death, stroke or myocardial infarction (MI) — between coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) with contemporary drug-eluting stents. Specifically, this composite outcome occurred in 22.0% of patients in the PCI arm and 19.2% of those in the CABG arm — a difference of 2.8 percentage points in favor of CABG (95% CI, –0.9 to 6.5 percentage points; P = 0.13)
Despite this statistical equivalence, the findings are more nuanced, argue the authors of the ACC.org analysis, Faisal Bakaeen, MD, of Cleveland Clinic, and Mario F.L. Gaudino, MD, PhD, of Weill Cornell Medicine.
In their analysis, Drs. Bakaeen and Gaudino highlight two features of the EXCEL trial’s design that they believe put CABG at a relative disadvantage:
Advertisement
The analysis authors also call attention to several noteworthy EXCEL findings beyond the primary outcome measure:
“The features of the study design that disadvantage CABG call for caution in interpreting the EXCEL trial’s finding of equivalence between the two revascularization strategies for low-complexity left main disease,” says Dr. Bakaeen. “Contemporary CABG that delivers complete revascularization with multiarterial grafting remains a highly compelling option for this patient population.”
The full expert analysis is available here.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable