Black and white patients realize similar gains following adoption of new protocol
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/bfd2dc43-1389-4236-874c-688a1b5af36a/23-HVI-3606665-CQD-650x450-1_jpg)
patient on gurney being rushed to emergency ward
Implementation of a comprehensive protocol for management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) similarly benefits Black and white patients, suggesting that widespread protocol adoption could help reduce traditional racial disparities in STEMI care delivery. So found a study that compared STEMI care metrics between these two groups before and up to five years after Cleveland Clinic adopted a comprehensive STEMI protocol. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
“This is the first study to show that a comprehensive STEMI protocol can successfully and equitably improve care for Black and white American patients,” says Umesh Khot, MD, Head of Regional Cardiovascular Medicine at Cleveland Clinic and corresponding author of the study. “Rapid identification of STEMI, development of standardized care protocols and procedural optimization were key components of the protocol, which yielded outcome gains across the board.”
It is well recognized that Black Americans with STEMI tend to receive poorer care compared with white Americans, with studies documenting transfer delays, lower rates of revascularization and longer door-to-balloon times. Such differences are believed to contribute to poorer STEMI outcomes among Black patients.
In July 2014, Cleveland Clinic implemented a comprehensive STEMI protocol designed to standardize care to improve process metrics and clinical outcomes among all patients.
The comprehensive STEMI protocol included the following major elements:
The study retrospectively examined medical records from consecutive patients with STEMI treated with PCI at Cleveland Clinic’s main campus, comparing those treated before the comprehensive STEMI protocol was adopted (January 1, 2011, to July 14, 2014) with those treated after protocol adoption (July 15, 2014, to July 15, 2019). The cohorts’ racial makeup was as follows:
Advertisement
Patients from other racial groups made up less than 1% of the identified population and were excluded.
Pre- and post-protocol cohorts were similar in age, sex and comorbidities, although fewer patients had a prior myocardial infarction in both post-protocol cohorts, and body mass index among white patients was higher in the post-protocol cohort.
Protocol adoption resulted in the following changes in key metrics among Black patients:
Regression models developed for each key process metric revealed no significant interaction with race. “Race was not found to be a factor in the benefits achieved after adopting the comprehensive STEMI protocol,” observes study co-author Grant Reed, MD, MSc, Quality Improvement Officer in Cleveland Clinic’s Section of Invasive and Interventional Cardiology. “This indicates that gains from the protocol were equitable between Black and white patients.”
Previous analyses of the effects of the adoption of Cleveland Clinic’s comprehensive STEMI protocol found that it also achieved benefits among other traditionally underserved groups. One study, published in the European Heart Journal Open and summarized in a Consult QD post, found that gains in key process metrics were made for men and women, eliminating the gender gap in most process and outcome metrics (table).
Advertisement
Another study (table) found that adoption of the comprehensive STEMI protocol reduced socioeconomic disparities not only in care process metrics but in clinical outcomes, most notably in-hospital mortality (complete study published in the Journal of the American Heart Association and summarized here).
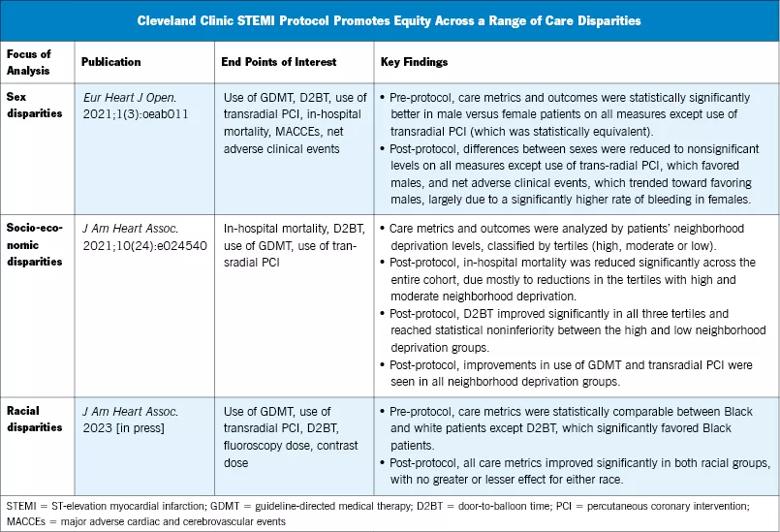
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/1c44d74b-4117-42a2-9401-c6fbf2f8a396/23-HVI-3606665_Inset_805x_jpg)
“These diverse studies on a single new approach to STEMI care indicate that standardizing healthcare delivery can benefit everyone, including traditionally underserved populations,” Dr. Khot concludes. “Establishing and adopting a comprehensive STEMI protocol like ours should be a major priority of hospital systems, especially those that serve large Black or socioeconomically disadvantaged populations. It’s encouraging that a single approach has been shown to reduce or eliminate disparities on three fronts — race, socioeconomic status and gender.”
Advertisement
Advertisement
A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery
Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation
Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable