Ultrasound brings unique utility to nerve entrapment syndromes
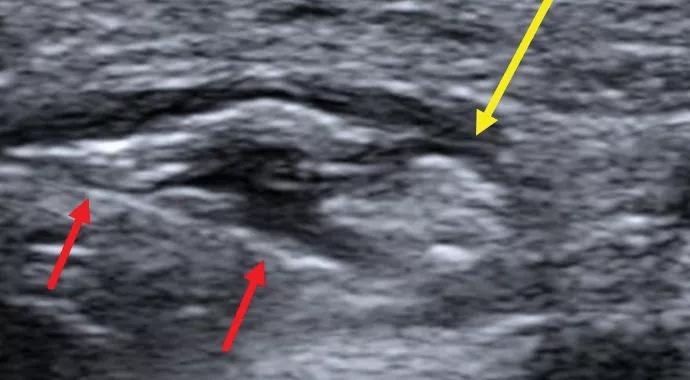
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/94f07ecb-cb77-4526-a78b-af3c88e0a829/Delzell-Patel-Hero-Image-690x380pxl_jpg)
Delzell-Patel-Hero-Image-690x380pxl
By Mital Patel, MD; Patricia Delzell, MD; Michael Forney, MD; Yuji Umeda, MD, PhD; and Jean Schils, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 34-year-old male healthcare worker presented with progressive bilateral dorsal-radial forearm and hand pain of one year’s duration. The pain was of burning character and in the distribution of the superficial branch of the radial nerve (SPN). The onset of symptoms correlated with a switch to electronic medical records at the patient’s workplace, requiring more typing. On physical examination, manual compression over the radial tunnel reproduced the patient’s symptoms. Forearm extensor strength was normal.
Initial imaging with MRI demonstrated no abnormal signal within the superficial branch of the radial nerve. However, subsequent ultrasound demonstrated a 3-cm segment of fascicular swelling with increased caliber of the SPN at the mid forearm between the brachioradialis, extensor carpi radialis longus, and pronator teres muscles, where the nerve exits the deep fascia (Figure 1). The radial nerve at the radial tunnel and posterior interosseous nerve were normal in appearance.

Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/5ad5f72f-997f-4091-a5e0-e7e7d28de664/Delzel-Inset-Image-Figure-1_No-Project-Number_jpg)
Figure 1. Transverse sonographic image demonstrating focal fascicular edema with increased caliber of the superficial branch of the radial nerve (yellow arrow).
Conservative management — including NSAIDs, splinting and physical/occupational therapy — failed to relieve the patient’s symptoms, so he elected to undergo an ultrasound-guided perineural steroid hydrodissection (Figure 2). After one month, the patient reported a 75 percent subjective improvement in symptoms with only mild modification of activity.
Advertisement
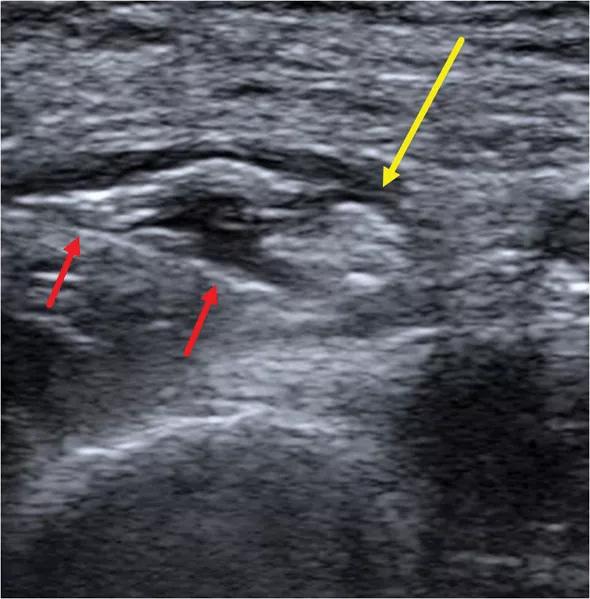
Image content: This image is available to view online.
View image online (https://assets.clevelandclinic.org/transform/518856c6-bada-4f48-8545-cbfb0505e8ea/Delzel-Image-of-Issue-Inset-Figure-2-590pxl-width_jpg)
Figure2. Transverse sonographic image demonstrating perineural hydrodissection with a 25-gauge needle (red arrows) of the superficial branch of the radial nerve (yellow arrow).
Entrapment of the SPN, classically referred to as Wartenberg syndrome, typically occurs secondary to friction between the mid-forearm muscle bellies and tendons as the nerve exits the deep fascia. The high spatial resolution of sonography allows for easier detection of subtle nerve abnormalities — such as fascicular swelling, epineural thickening and hyperemia — compared with MRI.
Additionally, sonography allows for real-time image-guided nerve therapies. Nerve hydrodissection displaces tendons and fascia surrounding the nerve by creating a perineural fluid plane, thus reducing friction. Concomitant steroid injection may help to reduce scar formation.
Our institution often uses ultrasound-guided nerve hydrodissection before surgical intervention for a variety of nerve entrapment syndromes, including those involving branches of the ulnar, radial, median, femoral, saphenous, peroneal, posterior tibial, plantar and iliohypogastric nerves.
Dr. Patel is a musculoskeletal fellow in Cleveland Clinic’s Imaging Institute.
Dr. Delzell is a musculoskeletal radiologist and the Director of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound in the Imaging Institute.
Dr. Forney is a musculoskeletal radiologist in the Imaging Institute.
Dr. Umeda is a medical orthopaedist in the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery.
Dr. Schils is Section Head of Musculoskeletal Radiology in the Imaging Institute.
Advertisement
Advertisement
New study advances understanding of patient-defined goals
Testing options and therapies are expanding for this poorly understood sleep disorder
Real-world claims data and tissue culture studies set the stage for randomized clinical testing
Digital subtraction angiography remains central to assessment of ‘benign’ PMSAH
Cleveland Clinic neuromuscular specialist shares insights on AI in his field and beyond
Findings challenge dogma that microglia are exclusively destructive regardless of location in brain
Neurology is especially well positioned for opportunities to enhance clinical care and medical training
New review distills insights from studies over the past decade