Why alternatives to surgery matter in radiation heart disease
By Brian Griffin, MD; Samir Kapadia, MD; and Douglas Johnston, MD
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
A 77-year-old man presented to Cleveland Clinic for a second opinion on his dyspnea that had begun two years earlier and had worsened significantly over the prior eight months. His complex medical history included thoracic radiation therapy for Hodgkin’s lymphoma in 1979. He subsequently developed coronary artery disease, which had been treated with stenting in 2009. He also suffered from renal insufficiency, due to having only one kidney, and Crohn’s disease.
We conducted a series of tests:
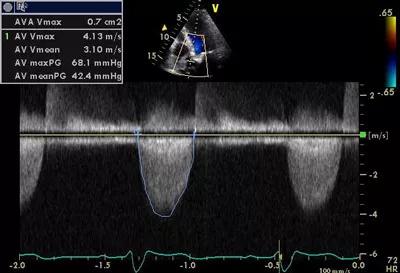
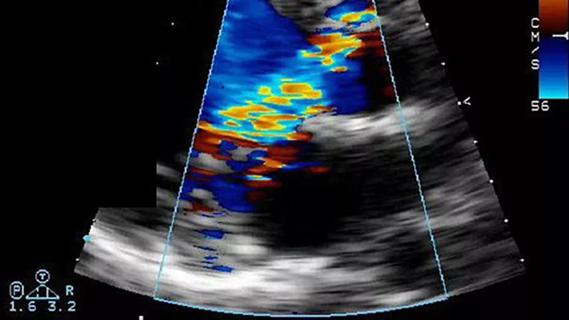
Figure 1. Echocardiography findings showing aortic velocity upon the patient’s presentation.
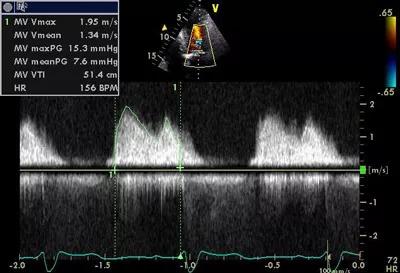
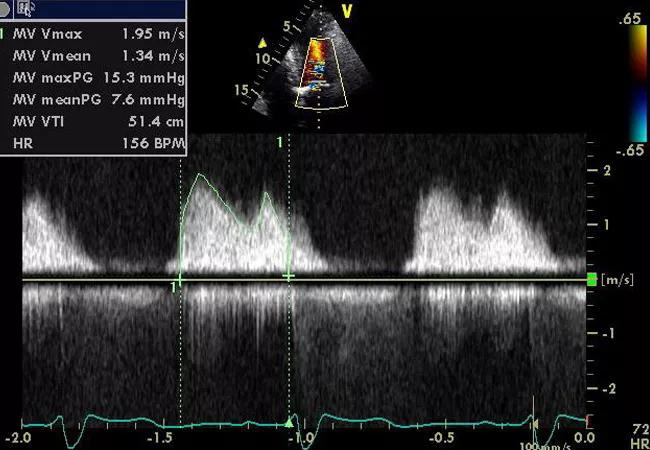
Figure 2. Continuous-wave Doppler echocardiogram of the patient’s mitral valve upon presentation.
Based on these test results, we determined the patient’s dyspnea was not caused by coronary disease but rather by calcific valve disease.
With complex patients like this, management decisions are best made by a multidisciplinary team including a cardiac imaging specialist, an interventional cardiologist and a cardiothoracic surgeon. Three treatment options were discussed in this case:
Advertisement
1) Surgical replacement of the aortic and mitral valves. Issues included:
2) Medical treatment only. Questions included:
3) Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR). Questions included:
The patient’s Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) risk score was calculated to be 17.4 percent, which made him a high-risk surgical candidate. Moreover, his brachiocephalic vein, distal ascending aorta, proximal arch and right ventricular myocardium all were located at an unsafe distance (4-5 mm) from the retrosternal midline. This significantly increased the risk of damage to his heart during surgery.
We believed the patient’s dyspnea could be relieved by improving blood flow through his aortic valve alone, given the significant stenosis present, so we determined he would be a good candidate for TAVR. Ideally, his mitral valve would have been replaced too, but this would have required open surgery, which we had eliminated as an option due to his STS risk score and the anatomical risk noted above.
TAVR was performed via transfemoral access without incident following balloon aortic valvuloplasty. The patient was left with a mild paravalvular leak, which improved on its own without intervention.
Advertisement
At his one-year checkup (see Figure 3), the patient was breathing better and feeling better, and he said he felt he was “back to normal.” His mitral valve, although still mildly narrowed, was not affecting his ability to exercise.
Figure 3. The patient’s echocardiography findings one year after TAVR.
Radiation therapy is known to cause extensive fibrosis and damage to the heart, lungs and great vessels. The following effects are common:
Radiation-associated heart disease is most common in patients who have received radiation for Hodgkin’s lymphoma or breast cancer. In addition to varying by volume of heart irradiated and time since radiation exposure, risk is further increased by the following factors:
In many ways, our patient illustrates the problems inherent in treating radiation-associated heart disease. First, clinicians must be alert to the possibility of radiation as an etiologic factor, which is best determined through a thorough medical history. Due to the extremely delayed nature of the side effects (our patient had been radiated 35 years earlier), any history of chest radiation should be considered a potential underlying cause.
Advertisement
Once the possibility of radiation-associated heart disease is identified, multidisciplinary team input should be sought to ensure the best treatment choice. These are difficult patients who require much thought, and a variety of expertise and experience can be invaluable.
Experience shows that radiation-associated heart disease portends increased long-term mortality following cardiothoracic surgery, as demonstrated by a retrospective Cleveland Clinic cohort study (Circulation. 2013;127:1476-1484) of patients undergoing cardiac surgery for radiation heart disease (n = 173) versus other etiologies of cardiovascular disease (n = 305). As shown in Figure 4, radiation heart disease was associated with significantly worse survival. The reasons for this finding are not well understood, although the combination of cardiac surgery and prior radiation may lead to compromised lung function and thereby compromise long-term outcomes, though immediate surgical mortality is low.
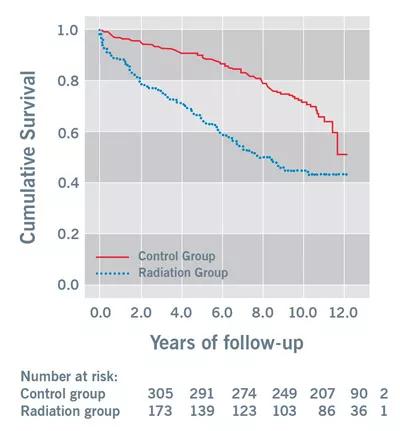
Figure 4. Kaplan-Meier curves showing significant differences in long-term mortality between patients with radiation heart disease who underwent cardiac surgery and a matched comparison cardiac surgery population. Reprinted with permission from Wu et al., Circulation (2013;127:1476-1484).
A key conclusion of our cohort study cited above was that alternatives to surgery may be required in radiation heart disease to improve long-term survival. This case underscores the imperative for treatment options in this risky patient population. It also demonstrates that for patients with severe aortic stenosis and a functioning mitral valve, TAVR can represent an excellent solution.
Advertisement
Dr. Griffin is Section Head of Cardiovascular Imaging. Dr. Kapadia is Section Head of Invasive and Interventional Cardiology. Dr. Johnston is a staff surgeon in the Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery.
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable