A new spin on collapse therapy overcomes devastating pneumonia

Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Of the approximately 7,000 patients I’ve treated as a thoracic surgeon, Danielle Abraham is the one that stands out. In 2009, Danielle was an active 28-year-old — a happily married mother of an 8-month-old daughter. Life was good, she said, until she contracted the H1N1 flu virus.
Since she was postpartum, it may have been her suppressed immune system that allowed the influenza to trigger a devastating bacterial pneumonia. A relentless cough and severe pain sent her to the hospital near her home in Buffalo, New York. For four weeks, she lay in the ICU in an induced coma. When her right lung collapsed, and then her left lung, she was flown to Cleveland Clinic.
When I first saw Danielle, the bacterial infection had begun to dissolve her lung tissue. Pneumatoceles had developed and had begun to rupture. Air was filling her pleural space. Even multiple chest tubes couldn’t keep up with the vigorous leak in her lungs. Air from the ventilator was coming straight out of the tubes.
We knew she could not be ventilated much longer.
It was late in the evening when we brought Danielle into surgery. We didn’t expect her to make it to the next morning on the ventilator.
At first, we tried reducing the pneumatoceles, but her lung tissue was so thin and diseased that our attempts to seal one hole just created more holes. The more we sewed or stapled, the worse the problem became. Within 15 minutes of opening her chest, we terminated our original plan and began brainstorming other ways to stabilize her.
Advertisement
In the 1930s, ’40s and ’50s, thoracic surgeons treated tuberculosis with collapse therapy, intentionally collapsing the lung. They believed that the tuberculosis bacteria would fail to thrive if denied oxygen, and lesions would heal if the lung were immobilized. Historically, surgeons would insert plombes, similar to plastic ping-pong balls, between the rib cage and the pleura, compressing the lung.
The concept worked — at least to resolve the tuberculosis. Unfortunately, it caused complications years later when the plombes began to erode or move. Putting biologically inert bodies into the thorax was not a lifelong solution.
While the technique was abandoned, the concept was still valid. And it’s ultimately what we used to help Danielle.
We attempted to press the inner lining of her rib cage onto her lung to control the air leak. Instead of using inert objects, we balled up a biomaterial mesh that typically dissolves in about six weeks. We hoped that would give Danielle’s pneumatoceles enough time to close before the lining would return to its normal position.
After closing up Danielle’s chest, we saw that the amount of air escaping from her chest tubes had decreased by 95 percent. Our plan was working.
Over the next several weeks, Danielle’s lungs healed and her infection responded to antibiotics. After nearly three months of being hospitalized, she returned to Buffalo to complete months of rehabilitation.
Her recovery was heroic, one that many couldn’t have endured. However, Danielle claims the hardest part was not seeing her daughter, including missing her first Halloween, her first Thanksgiving and her first steps. I believe Danielle’s family inspired her to fight as well as she did.
Advertisement
When she returned for a follow-up months later, I was shocked. I had only known her as a patient on a ventilator. Now she was back to being the lively wife and mother she had been before her illness.
I had thrown a medical Hail Mary, but she had caught it and scored a touchdown. Her own drive and determination had cured her.
CT scans showed no residual evidence of our procedure. The mesh plombes were completely gone. Although she did lose about 50 percent of lung function due to the infection, she has been able to lead a normal life with moderate physical activity.
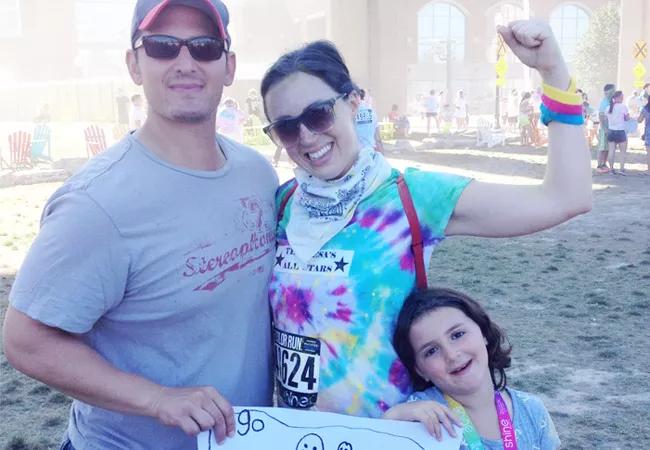
When I last saw her, she had recently walked a 5K (photo).

Danielle with her husband and daughter.
Since Danielle’s surgery, we have used the same technique successfully on other critically ill patients with similar problems.
Having performed thousands of operations in my career, I wish I could say I’ve seen it all. But there will always be unexpected circumstances to keep me — and all of us — learning and innovating.
Going into surgery with a Plan A isn’t enough. We also need Plans B, C and D. (For Danielle, Plan C was to pack gauze into her left lung, hoping her right lung would carry her until cavities in the left lung scarred over. Plan D was to remove her left lung. I doubt either of those plans would have had outcomes as favorable.)
Everything we learn as physicians, no matter how seemingly trivial or historically insignificant, could become vitally important someday. When it comes to saving a life, sometimes we need every tool in the shed — including plain common sense.
Advertisement
Dr. Murthy is the Daniel and Karen Lee Endowed Chair in Thoracic Surgery, Section Head of Thoracic Surgery and Surgical Director of the Center of Major Airway Disease at Cleveland Clinic.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
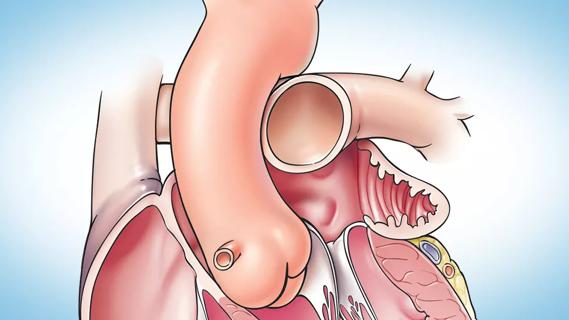
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
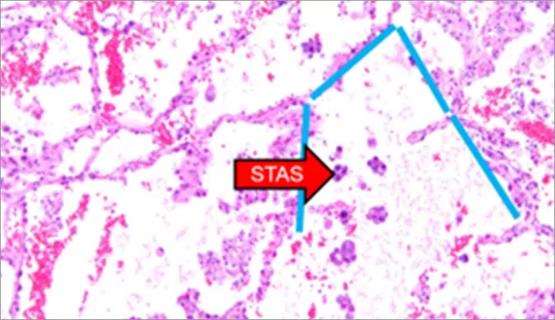
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
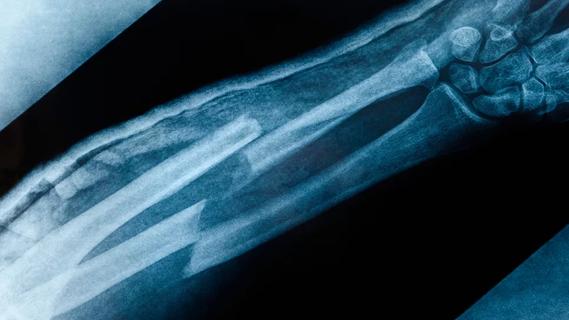
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
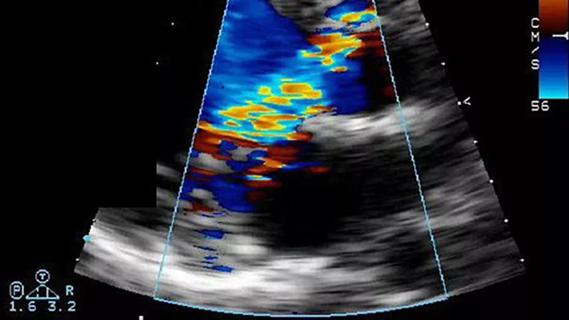
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable