‘Lifetime strategy’ entails valve repair — or replacement with a bioprosthesis
Bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) is an anomaly occurring in 1 to 2 percent of births. Patients with BAV generally function well until midlife, when symptoms of aortic insufficiency or aortic stenosis appear. This generally prompts referral for valve replacement with a mechanical prosthesis.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
With extensive experience in treating BAV disease, Cleveland Clinic surgeons recommend a different approach: valve repair for patients with aortic insufficiency, and valve replacement with a bioprosthesis for patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis and those whose valves cannot be repaired. Both approaches offer excellent short- and long-term outcomes.
“Our overall strategy is to help patients live a long, healthy, active life without the burden of anticoagulation,” says Cleveland Clinic cardiothoracic surgeon Lars G. Svensson, MD, PhD, Chair of Cleveland Clinic’s Heart & Vascular Institute.
Cleveland Clinic is one of a select number of U.S. centers offering repair of BAV in patients with aortic insufficiency. A recent review of 728 BAV repairs at Cleveland Clinic from 1985 to 2011 found the operation to be safe, with low rates of hospital mortality (0.41 percent) and stroke (0.27 percent). The procedure was also durable, with 78 percent of patients free from AV reoperation at 10 years. Results in recently operated patients are even better.
“Repairs that failed tended to do so within 12 to 18 months,” says Dr. Svensson, who was principal author of the review. “In these cases, the risks associated with reoperation were low, and there were no deaths from reoperation.” The 10-year survival rate was 94 percent.
“Repair is the best option for avoiding anticoagulation,” he adds. “Unfortunately, only 65 to 70 percent of leaky valves can be repaired. Once the leaflets have started to thicken from calcium and the lumen narrows, repair is no longer possible.”
Advertisement
Often, patients are not referred for aortic valve surgery until they are severely symptomatic. According to Dr. Svensson, it’s a misconception that patients must be highly symptomatic to benefit. “Evidence shows that hearts start to develop changes in structure and function before symptoms appear,” he says. “Patients who wait until symptoms develop before undergoing surgery do worse than those who have surgery early.”
Major barriers to early surgical referral include fear of pain and a difficult recovery with sternotomy, as well as the need for anticoagulation with a mechanical valve. “Although most patients do not have a great deal of pain and difficulty recovering from a sternotomy, minimally invasive surgery makes the recovery easier,” Dr. Svensson notes. “However, anticoagulation definitely requires lifestyle changes, which is why we like to avoid mechanical valves whenever possible.”
While mechanical valves are the standard recommendation for AV replacement in younger patients, these valves require lifelong anticoagulation. Anticoagulants are associated with a higher incidence of bleeding complications, and lifelong anticoagulation distresses patients. For patients with symptomatic aortic stenosis, a biological valve offers excellent durability without the need for anticoagulation.
Dr. Svensson and colleagues recently published a review of 12,569 patients with AV disease who received the Carpentier-Edwards Perimount bovine prosthesis at Cleveland Clinic. In this study, the largest series of biological valve recipients ever reported, mortality was less than 0.5 percent, and short- and long-term outcomes were excellent.
Advertisement
In older patients, explantation for structural valve deterioration (SVD) was rare and unlikely to have been affected by valve size or implant technique. SVD was more common in patients under age 60; however, durability was very good, with 55 percent freedom from SVD at 20 years.
“I feel strongly that we must offer patients the option of a valve that does not require anticoagulation, particularly because all evidence says survival is the same with mechanical and tissue valves,” says Dr. Svensson.
Although the Perimount prosthesis has served patients well for nearly 30 years, newer bovine valves such as Edwards Lifesciences’ GLX valve, currently being evaluated in the COMMENCE trial, and new operative techniques are likely to further extend valve life. Dr. Svensson is the national principal investigator of COMMENCE.
Valve repair and bioprosthetic valve replacement are part of a strategy to ensure that patients with BAV get back on their feet as quickly as possible without compromising their future needs.
When valve replacement is performed without another surgery requiring sternotomy, Cleveland Clinic surgeons perform the procedure minimally invasively (Figures 1 and 2).
“With a sternal-sparing right thoracotomy or minimally invasive ‘J’ incision, patients are back to normal activity faster,” Dr. Svensson explains. “Because less scar tissue forms after minimally invasive operations, patients’ risk is lower if they need an operation later. Should the patient need reoperation in the future, we know we can do it very safely. In the meantime, they can lead a totally normal life.”
Advertisement
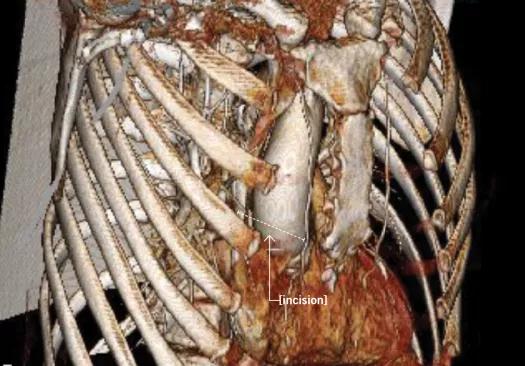
Figure 1. A CT with 3-D reconstruction allows surgeons to choose the optimal incision and plan for the safest operation. Here, a sternal-sparing minithoracotomy incision allowed excellent access to the aortic valve.
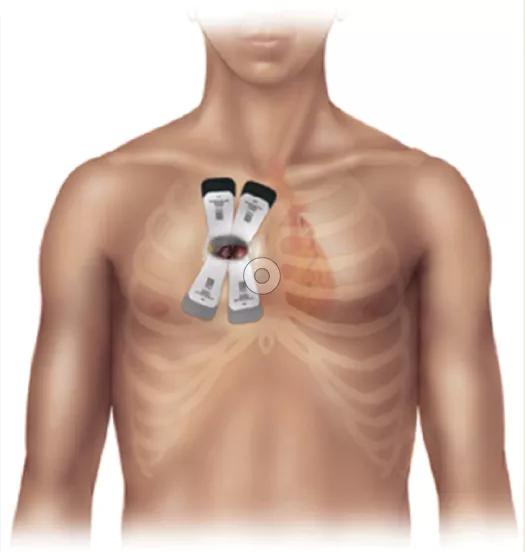
Figure 2. Many patients needing isolated aortic valve replacement are eligible for a sternal-sparing approach with a 5- to 6-cm incision in the right chest.
While avoiding reoperation has been the major impetus to implant mechanical valves in younger patients, decreasing mortality rates for cardiac reoperation and the development of valve-in-valve transcatheter technology have altered this perception.
“Many younger patients who prefer to avoid lifelong anticoagulation may find the SVD risk reported in our study acceptable,” says Dr. Svensson. “Younger, active patients need a valve that will keep up with them and allow them to pursue whatever activities they choose without anticoagulation limiting their lifestyle. Ideally, bicuspid valves should be repaired at centers that have extensive experience in their repair because great care is needed when repairing a valve to achieve an optimal durable result.”
Dr. Svensson expects to see increased use of biological valves for AV replacement in patients for whom repair is not feasible.
“Newer valves hold the promise of better long-term durability in younger patients,” he notes. “In addition, we are able to successfully place a new transcatheter aortic valve in a previously replaced valve by remote access via the groin.”
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable