Averts need for lifelong anticoagulation
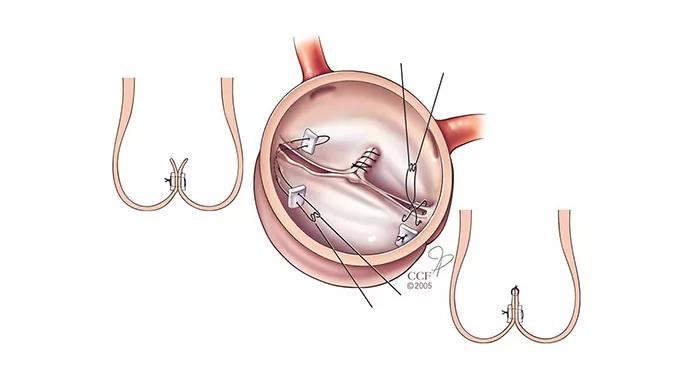
Bicuspid aortic valve (BAV) is the most common congenital cardiac abnormality. In early- to mid-adulthood, patients often present with symptoms of valvular regurgitation that may include dyspnea and enlarging heart.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Although replacement with a mechanical valve is commonly recommended, a study conducted at Cleveland Clinic found that BAV repair carries a low risk of death, stroke and reoperation. Moreover, avoidance of a prosthetic valve prevents the need for lifelong anticoagulation and its associated risks.
The study included all 728 patients who underwent aortic valve repair for congenital BAV disease at Cleveland Clinic from 1985 to 2011. Of these, 70 percent had aortic valve regurgitation. The mean age at time of surgery was 42.5 years.
The risk of hospital mortality was 0.41 percent. The risk of stroke was even less at 0.27 percent, and rates of endocarditis and bleeding were also low.
“Our results show that bicuspid aortic valve repair can be achieved with low risk,” says cardiothoracic surgeon Lars Svensson, MD, PhD.
Ten years after valve repair, 94 percent of patients were still alive, and 78 percent had remained free from reoperation. At 20 years, 82 percent were still alive.
At Cleveland Clinic, all bicuspid aortic valves are repaired in a minimally invasive “keyhole” operation. Patients are discharged home four to seven days after surgery and can return to driving—and often to work—in as little as two weeks.
Of the 728 patients in the registry, 38 percent had aneurysms of the ascending aorta, which were repaired at the time of aortic valve repair. At five years, freedom from reoperation was 89 percent for repair alone and 87 percent for repair plus aortic procedure. Patients who had undergone surgery more recently had even better results.
Advertisement
“We believe that aortic aneurysms greater than five cm should be fixed at the time of valve repair,” says Dr. Svensson.
Results of the Cleveland Clinic study, published in May 2014 Annals of Thoracic Surgery, may put to rest any questions about the procedure’s durability. Ten years after repair, 91 percent of patients still had their native valve.
“Many will probably need a replacement later, maybe 20 years after surgery, but repair enables us to hold it off. Most of these patients are young at the time of repair, so we were able to spare them from being on Coumadin for life,” says Dr. Svensson.
No deaths were seen in the group of patients who underwent valve replacement late after repair. “Hence, the life expectancy for these patients is excellent,” he says.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
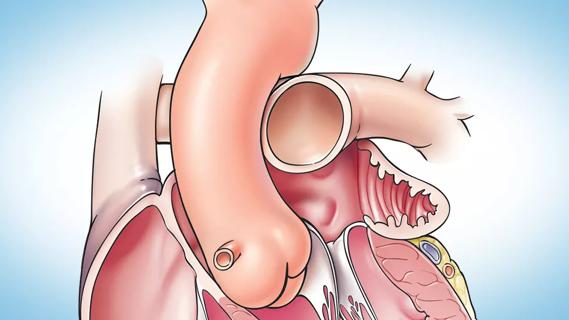
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
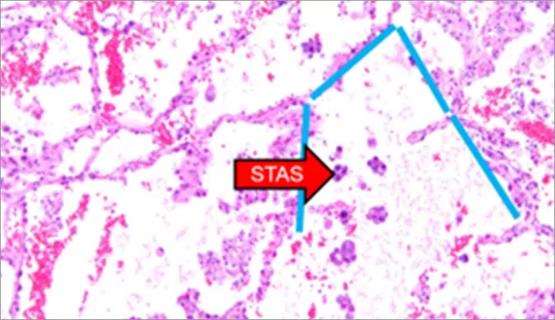
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
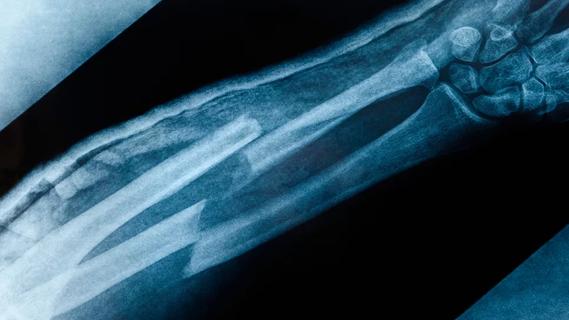
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
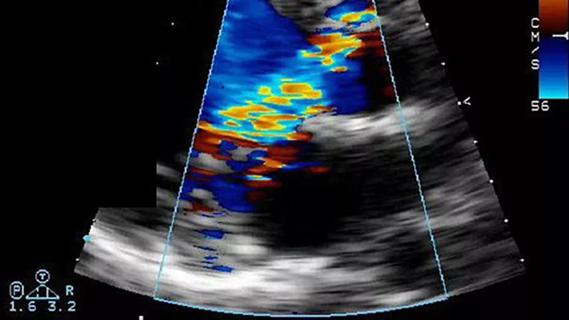
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
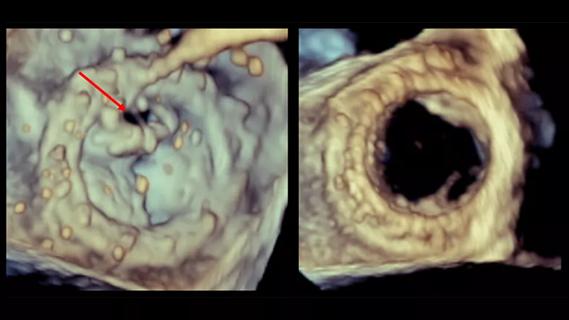
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable