Nearly two-thirds of patients see clinically meaningful gains in large series
For many patients with epilepsy, surgery is the best option for relief of intractable seizures. While complete freedom from seizures is the ultimate goal of any epilepsy therapy, it is not always achieved — and is not the only worthwhile treatment goal. Another way of looking at therapy success is improved quality of life, regardless of seizure count.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
Cleveland Clinic Epilepsy Center staff recently reviewed quality-of-life assessments in 461 patients treated surgically for epilepsy at the center between 2007 and 2016. The assessments were done using the 10-item, patient-completed Quality of Life in Epilepsy questionnaire (QOLIE-10). This validated tool covers general and epilepsy-specific aspects of quality of life, including memory, physical and mental effects of medications, mental health (energy, depression, overall quality of life) and social functioning (fear of seizures, social and work limitations). A lower QOLIE-10 score is associated with better quality of life.
As shown in the graph below, these patients’ mean QOLIE-10 score fell from 27.9 at baseline to 22.5 at last follow-up, a nearly 20 percent improvement (P < .0001). The mean duration of follow-up was 36.3 months, with all patients assessed at least six months following surgery. The standard box plots reflect the median scores and the 25th and 75th quartiles.
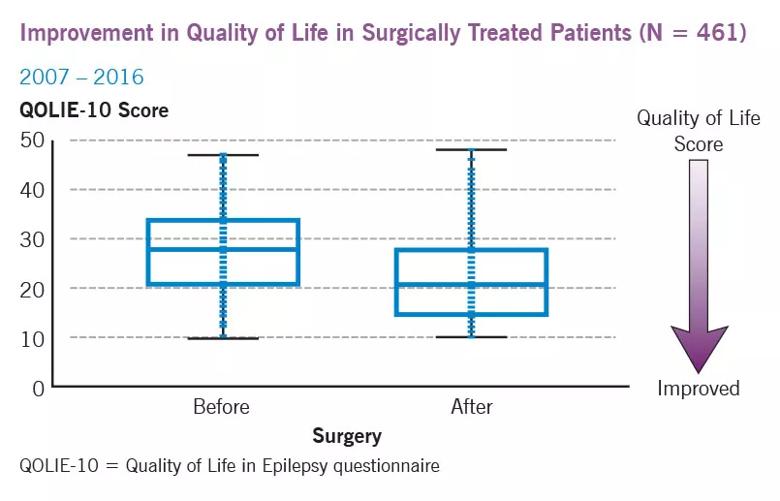
Quality-of-life improvements are considered to be clinically meaningful if QOLIE-10 scores drop by at least 10 percent from baseline. Using that as a threshold, 64 percent of surgically treated patients achieved clinically meaningful improvement. By comparison, 44 percent of medically treated patients achieved clinically meaningful improvement (based on data from 3,810 patients between 2007 and 2016).
“Patients are included in our outcomes data whether or not their treatment resulted in freedom from seizures,” says Lara Jehi, MD, Director of Outcomes Research for the Epilepsy Center. “Although much of the improvement can be attributed to achieving seizure freedom, we are increasingly realizing that patients can significantly benefit even if they are not completely cured of their epilepsy.”
Advertisement
She notes that about 50 to 65 percent of patients with previously medically intractable epilepsy remained seizure-free more than 10 years after surgical treatment at Cleveland Clinic, as detailed in a previous Consult QD post. Outcomes differed by site of surgery.
Dr. Jehi is currently leading a five-year, $3.4 million National Institutes of Health grant to develop a tool to predict individual outcomes in epilepsy surgery (see previous post). The nomogram, or risk calculator, will help physicians determine which patients are most likely to benefit from surgery in terms of improved seizure control. Based on the quality-of-life research findings, Dr. Jehi intends to expand the nomogram to also include a predictor of which patients are most likely to experience improved quality of life following epilepsy surgery.
“Defining surgical success solely as 100 percent seizure freedom is a high bar and can result in turning away patients who may benefit from surgery but are unlikely to meet that threshold,” explains Dr. Jehi. “We can help more patients if we also include quality of life as an important goal for treatment.”
She notes that routine collection of outcomes data by Cleveland Clinic is critical to her work in developing risk calculators. “Without such data, we would not be able to develop useful predictors at an individual level,” she adds. “Patients don’t want to hear about averages — they want to know how surgery will affect them. With good data, we can come closer to providing them with that information.”
Advertisement
More outcomes data from the Epilepsy Center are available in Cleveland Clinic Neurological Institute’s 2016 Outcomes Book.
Advertisement
Advertisement

New study advances understanding of patient-defined goals

Testing options and therapies are expanding for this poorly understood sleep disorder
Real-world claims data and tissue culture studies set the stage for randomized clinical testing
Digital subtraction angiography remains central to assessment of ‘benign’ PMSAH
Cleveland Clinic neuromuscular specialist shares insights on AI in his field and beyond

Findings challenge dogma that microglia are exclusively destructive regardless of location in brain

Neurology is especially well positioned for opportunities to enhance clinical care and medical training
New review distills insights from studies over the past decade