Internet-fueled misinformation demands broad physician response

It’s time to call out the forces behind low statin adherence for what they are: an internet-driven “cult of statin denial” with deadly consequences.
Advertisement
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cleveland Clinic products or services. Policy
So argues Cleveland Clinic Cardiovascular Medicine Chair Steven Nissen, MD, in a new Annals of Internal Medicine editorial.
“Statins have developed a bad reputation with the public, a phenomenon driven largely by proliferation on the Internet of bizarre and unscientific but seemingly persuasive criticism of these drugs,” writes Dr. Nissen. As one sign of the extent of the phenomenon, he cites these sobering stats: The 655,000 search engine results yielded by the term statin benefits are utterly dwarfed by the 3,530,000 results produced by the term statin risks.
“We are losing the battle for the hearts and minds of our patients to Web sites developed by people with little or no scientific expertise,” he continues, noting that these sites primarily propagate one or both of two key notions:
Far too often the result is that patients discontinue their statin therapy or forgo it in the first place, resulting in “shockingly low” statin adherence rates that often have grave consequences, Dr. Nissen argues.
The latest evidence comes from a cohort study by Zhang and colleagues published in the same Annals of Internal Medicine issue. Over four years of follow-up, these researchers documented 1 excess cardiovascular event for every 59 patients who discontinued statin therapy and 1 excess death for every 83 patients who discontinued statin therapy (relative to comparable patients who continued their statin therapy).
Advertisement
Dr. Nissen points out that this is the latest in a long line of studies suggesting that statin nonadherence has serious consequences. While all these investigations have limitations as observational, retrospective studies that largely rely on administrative data, the consistency of their findings is compelling.
This leads him to conclude that “[p]assive acceptance of harmful pseudoscience is not an option.” He argues that thoughtful physicians “must work together to educate the public and enlist media support, and we must take the time to explain to our patients that discontinuing statin treatment may be a life-threatening mistake.”
Dr. Nissen’s full editorial is available here. And check out this companion infographic that lays out the numbers behind — and stakes of — the statin denial phenomenon.
Advertisement
Advertisement

A sampling of outcome and volume data from our Heart & Vascular Institute
Concomitant AF ablation and LAA occlusion strongly endorsed during elective heart surgery

Large retrospective study supports its addition to BAV repair toolbox at expert centers
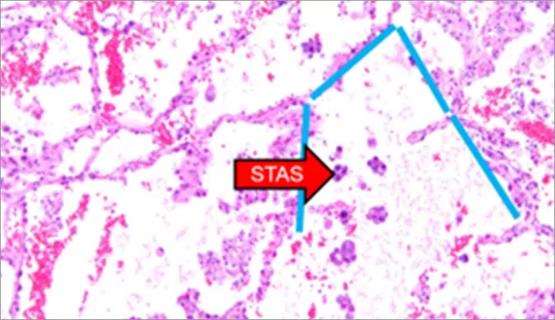
Young age, solid tumor, high uptake on PET and KRAS mutation signal risk, suggest need for lobectomy
Surprise findings argue for caution about testosterone use in men at risk for fracture
Residual AR related to severe preoperative AR increases risk of progression, need for reoperation

Findings support emphasis on markers of frailty related to, but not dependent on, age
Provides option for patients previously deemed anatomically unsuitable